Figure 4.
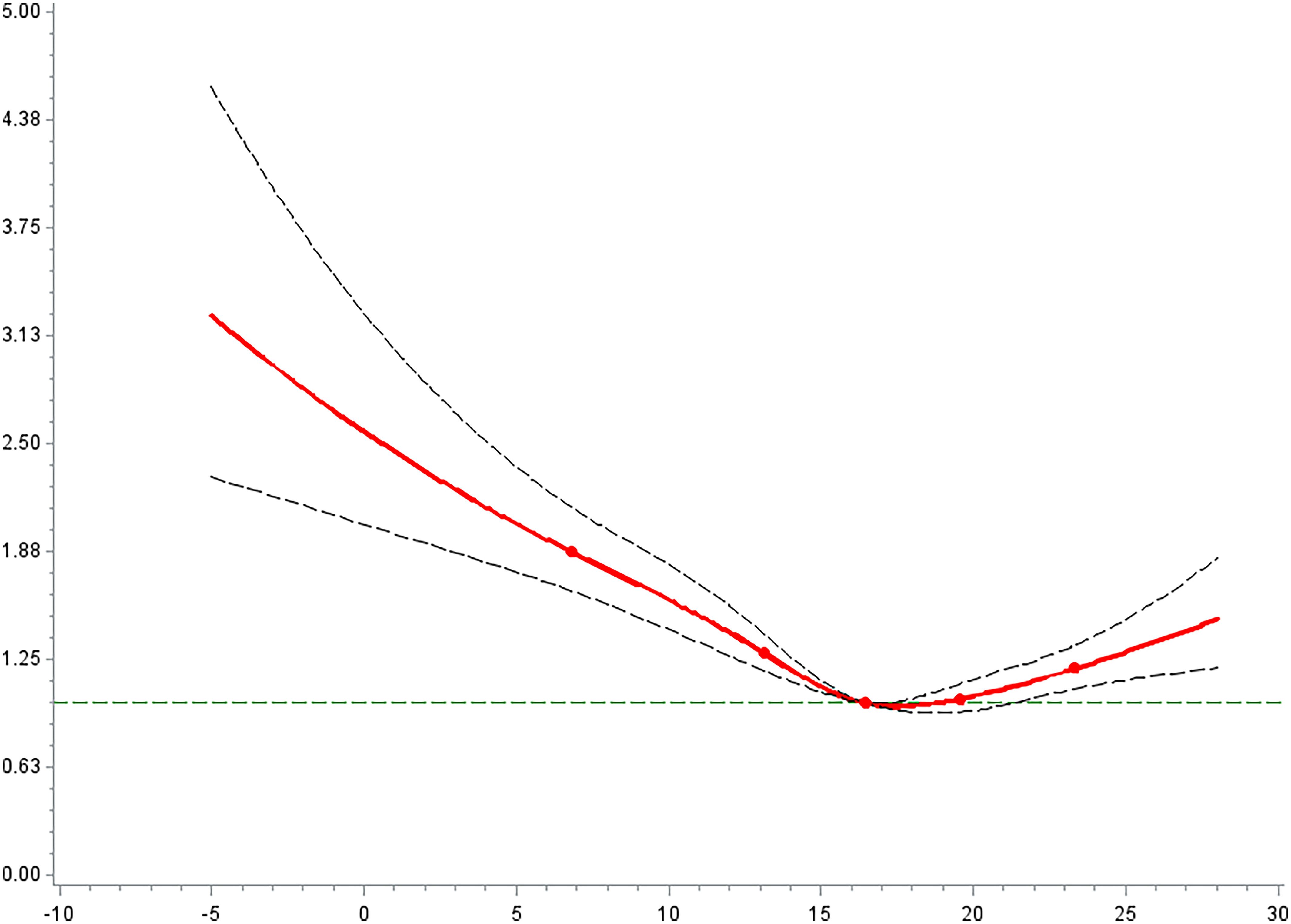
The relationship between the average temperature exposed during the whole pregnancy and the preterm birth risk in China Labor and Delivery Survey (). (See Tables S9 for corresponding numeric data.) Note: Cox proportional hazard regression incorporated with penalized cubic spline was used to examine exposure-response associations. HRs represent a 1-unit increase in extreme weather events and are presented with a 95% CI. All models were adjusted for maternal age, maternal ethnicity, maternal education, insurance type, child sex, parity, GDP per capita, geographic region, conception season, conception year, , and . CI, confidence interval; GDO, gross domestic product; HR, hazard ratio; , particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter .
