Figure 4.
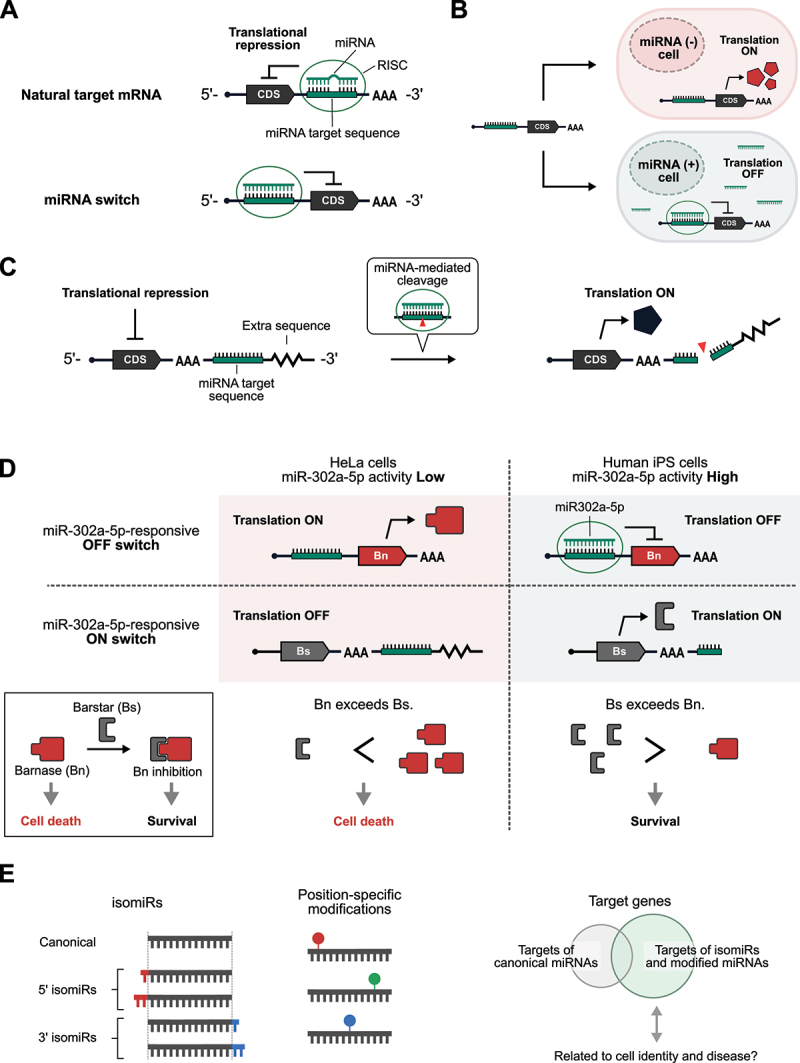
mRNA-based miRNA sensors.
(A) MicroRNA (miRNA) usually binds to target sequences in the 3’-UTR of target mRNAs with imperfect miRNA – mRNA complementarity (top). miRNA-loaded RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex) recognizes target mRNAs and represses their translation. For miRNA switches, target sequences complementary to miRNAs are inserted into the 5’-UTR (bottom). CDS: coding sequence.
(B) Distinguishing different cell types based on miRNA activities. (C) Schematic illustration of miRNA-responsive ON-type switches. (D) Combinatorial use of miRNA-responsive OFF-type switch and ON-type switch for efficient elimination of undesired cells. (E) IsomiRs and modifications in miRNA diversify the regulatory roles of miRNAs. Further studies are needed to elucidate the relationship between these alterations, cellular identity, and diseases.
