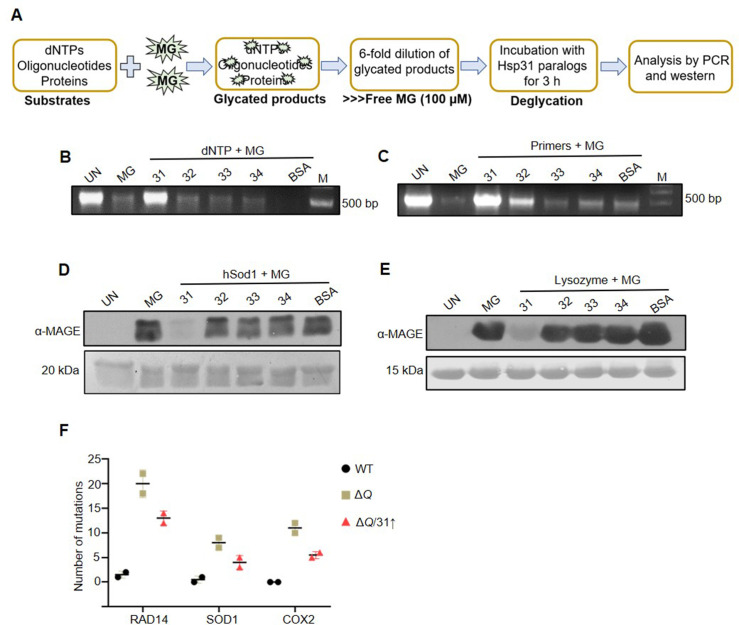
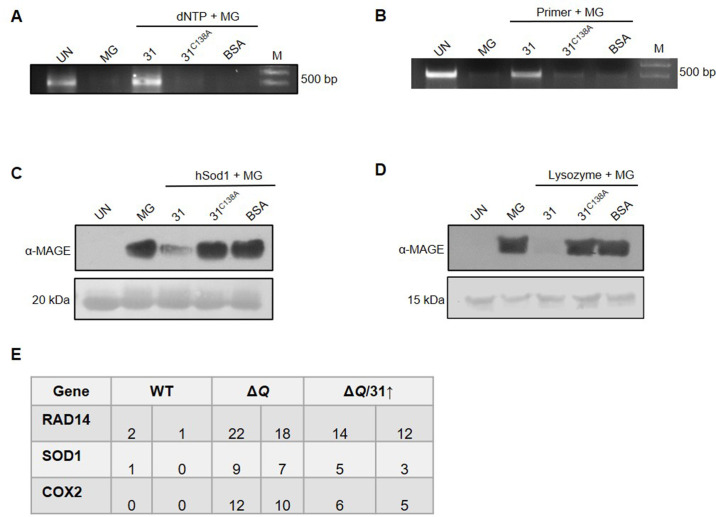
Figure 6. Hsp31 repairs MG-derived AGE modifications on DNA and proteins.
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental procedure used for DNA and protein deglycation reactions. (B, C) DNA deglycation by Hsp31. 500 µM dNTPs (B) or 150 µM forward and reverse primers (C) were incubated without (UN) or with 2 mM MG for 2 hr. Subsequently, 5 µg Hsp31 paralogs were added and incubated for 3 hr. The samples were subjected for PCR analysis. (D, E) Hsp31 reverts MG modification on proteins. hSod1 (D) and Lysozyme (E) were glycated for 2 hr with 2 mM MG and incubated with Hsp31 paralogs. The glycation status was determined through western analysis against anti-MAGE antibody. 10 kb DNA ladder was used as a marker (M) for DNA gels, and the Ponceau S stain indicates the equal loading of protein samples. BSA was used as a negative control in all experiments. The experiments were performed in three independent biological replicates. (F) The dual role of Hsp31 reduces MG-induced DNA mutations. Respective genes were PCR amplified, and Sanger sequenced from strains treated with 10 mM MG. The number of genetic mutations was plotted on GraphPad prism 5.0 (n=2).