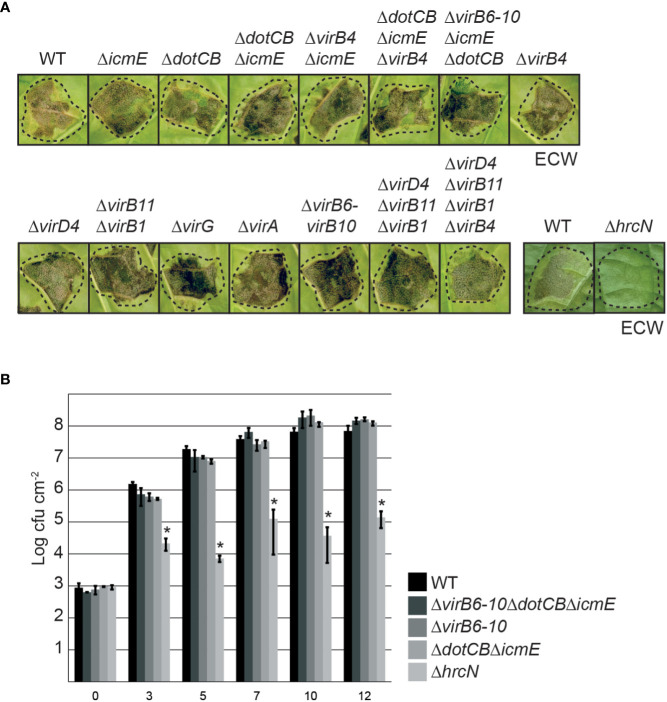
Figure 4.
The putative Vir- and Icm/Dot-like T4S systems do not significantly contribute to virulence of X. euvesicatoria. (A) Infection studies with X. euvesicatoria wild-type, hrcN and T4S mutant derivatives. Strain 85-10 (wt) and deletion mutant derivatives thereof lacking the T3S ATPase gene hrcN or single or multiple vir and icm/dot genes as indicated were infiltrated at a density of 108 cfu ml-1 into leaves of susceptible ECW pepper plants. Disease symptoms were photographed 7 dpi. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated leaf areas. The experiment was performed three times with similar results. (B) In planta growth of wild-type and T4S mutant derivatives of X. euvesicatoria. Strain 85-10 (wt) and deletion mutant derivatives thereof lacking single or multiple vir and icm/dot genes as indicated were infiltrated into leaves of three susceptible ECW pepper plants. Bacterial in planta growth was monitored over a period of 12 days. The T3S-deficient and non-pathogenic strain 85-10ΔhrcN, which lacks the ATPase of the T3S system, was analyzed as control. Mean values of cfu/cm2 and standard deviations from one experiment are depicted in the diagram. The experiment was performed three times with similar results. According to a one-tailed paired t-test, the difference in growth of X. euvesicatoria wt and hrcN deletion mutant strains is significant (with a p value of 0.024; indicated by asterisks). Growth of T4S mutants is not significantly different from that of the wild-type strain (p values of 0.075 for strain 85-10ΔvirB6-10ΔdotCBΔicmE, 0.121 for strain 85-10ΔvirB6-10 and 0.134 for strain 85-10ΔdotCBΔicmE).