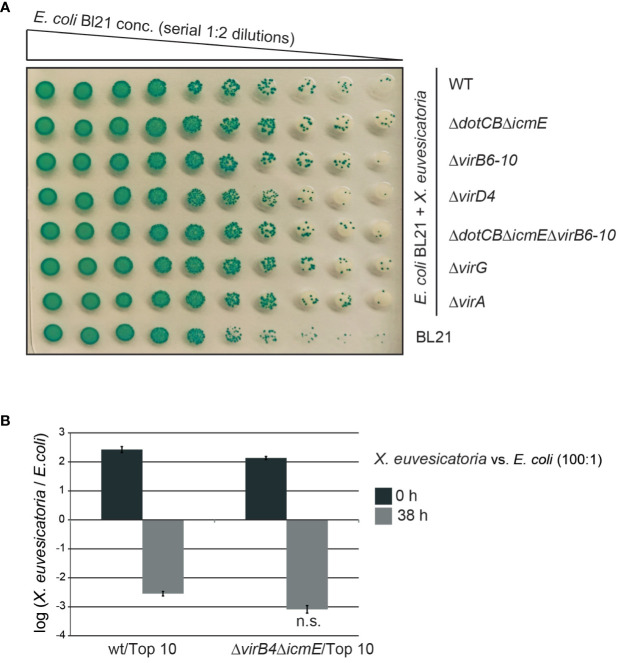
Figure 5.
In vitro growth of E. coli is unaffected by X. euvesicatoria. (A) Cocultivation with X. euvesicatoria strains does not affect in vitro growth of E. coli. Serial dilutions of E. coli strain BL21, which naturally expresses the β-galactosidase, were incubated with X. euvesicatoria strain 85-10 (wt) or deletion mutant derivatives thereof lacking single or multiple vir and icm/dot genes as indicated. X. euvesicatoria strains were incubated at initial concentrations of 5 × 108 CFU/ml with E. coli BL21 at a concentration of 5 × 106 CFU/ml or serial 1:2 dilutions on LB agar plates containing X-gal and IPTG overnight. One representative image is shown. The experiment was performed three times with similar results. (B) Ratio of X. euvesicatoria and E. coli cells after cocultivation. X. euvesicatoria strain 85-10 (wt) or 85-10ΔicmEΔvirB4 and E. coli strain Top 10 were mixed at a ratio of 100: 1, spotted on an LB agar plate and serial dilutions were plated after 0 and 38 hours on NYG medium with rifampicin for X. euvesicatoria strains and on LB medium with streptomycin for growth of E. coli to count bacterial colonies. Mean values and standard deviations of the ratio of X. euvesicatoria and E. coli colonies from one representative experiment are shown. According to a t-test, the difference in growth of E. coli in the presence of the X. euvesicatoria wt or the T4S mutant is not significant (n.s.; p value of 0.2487). The experiment was performed three times with similar results.