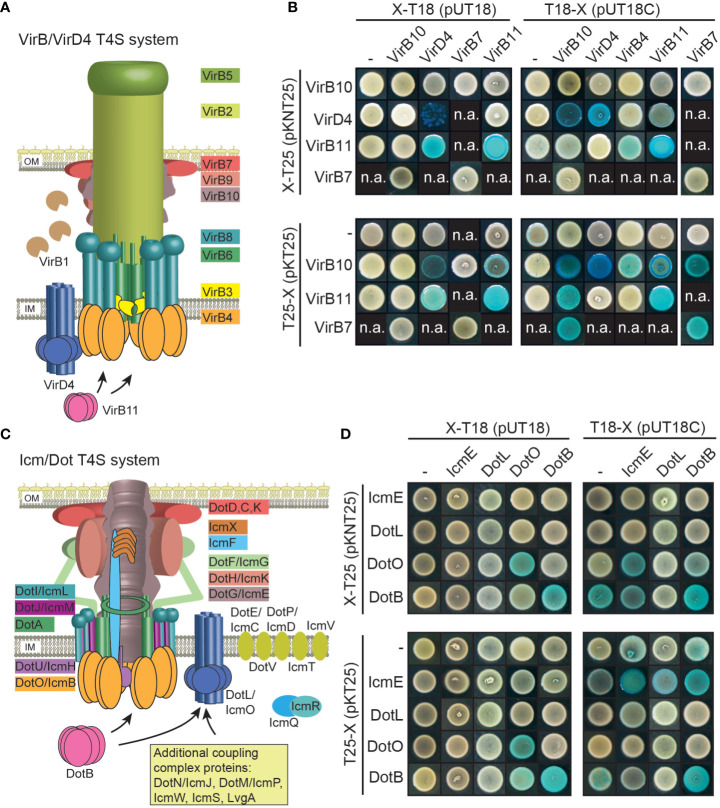
Figure 7.
Vir and Icm/Dot proteins from X. euvesicatoria assemble into oligomeric complexes. (A) Schematic representation of the VirB/VirD4 T4S system. The model was adapted according to Mace et al., 2022. IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane. (B) Results of BACTH assays with Vir proteins from X. euvesicatoria. T18 and T25 fusions of the predicted structural components VirB7 and VirB10 as well as of the putative ATPases VirD4, VirB4 and VirB11 were analyzed in E. coli BTH101 cells as indicated and bacterial cultures were grown on indicator plates containing X-gal and IPTG. As control, fusion proteins were tested against the T18 or T25 domain alone as indicated. All proteins were stably synthesized as was shown by immunoblot analysis of bacterial cell extracts, using a FLAG epitope-specific antibody (see Figure S1 ). n.a., not analyzed. Interaction studies were performed at least three times with similar results. One representative colony is shown. Results are summarized in Table 2 . (C) Schematic representation of the Icm/Dot-type T4S system. The model was adapted according to previous publications (Christie et al., 2017; Ghosal et al., 2019; Gomez-Valero et al., 2019; Sheedlo et al., 2022). IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane. (D) BACTH assays with Icm/Dot proteins from X. euvesicatoria. T18 and T25 fusions of the predicted structural component IcmE and the putative ATPases DotL, DotO and DotB were analyzed as described in (B). All proteins were stably synthesized as was shown by immunoblot analysis of bacterial cell extracts, using a FLAG epitope-specific antibody (see Figure S1 ). n.a., not analyzed. Interaction studies were performed at least three times with similar results. Results are summarized in Table 2 .