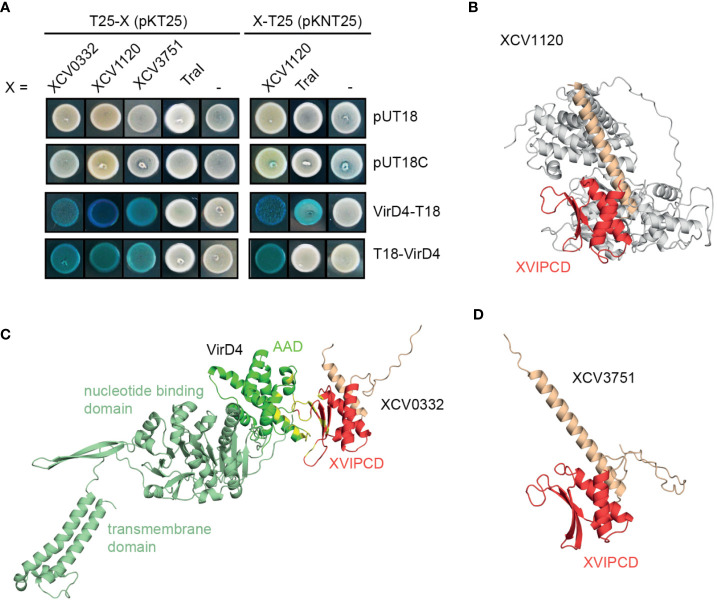
Figure 8.
Candidate T4S substrates from X. euvesicatoria interact with VirD4 and contain a predicted ααβββ motif in the C-terminal XVIPCD. (A) Candidate T4S substrates from X. euvesicatoria interact with VirD4 in BACTH-based interaction studies. The interaction of T18 and T25 fusions of the candidate T4S substrates XCV0332, XCV1120, XCV3571 and TraI with VirD4 was analyzed in E. coli BTH101 cells as indicated and bacterial cultures were grown on indicator plates containing X-gal and IPTG. As control, fusion proteins were tested against the T18 or T25 domain alone as indicated. All tested proteins were stably synthesized as was shown by immunoblot analysis of bacterial cell extracts, using a FLAG epitope-specific antibody (see Figure S1 ). Interaction studies were performed at least three times with similar results. One representative colony is shown. (B) Structure prediction of VirD4 and in complex with the T4S substrate XCV0332 from X. euvesicatoria. Structures were predicted using the AlphaFold 2 algorithm and visualized using PyMOL (https://pymol.org). The AAD from VirD4 is shown in dark green, the ααβββ motif in the XVIPCDs of XCV0332 is shown in red. Residues predicted to be involved in the interaction between the AAD from VirD4 and the XVIPCD of XCV0332 are shown in yellow. (C) Structure prediction of XCV1120 from X. euvesicatoria. using the AlphaFold 2 algorithm. The ααβββ motif in the XVIPCDs is shown in red. (D) Structure prediction of XCV3751 from X. euvesicatoria. using the AlphaFold 2 algorithm. The ααβββ motif in the XVIPCDs is shown in red.