Fig. 2.
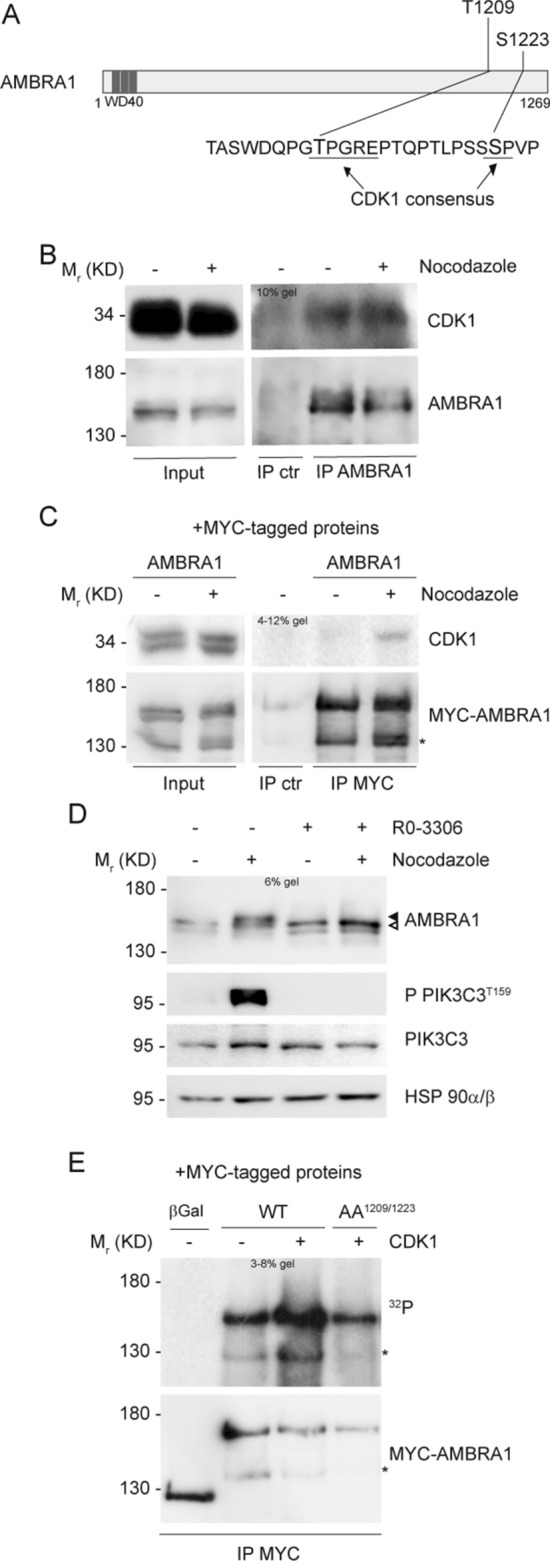
CDK1 phosphorylates AMBRA1 at T1209 and S1223. A Schematic representation of AMBRA1 protein, highlighting T1209 and S1223 with their respective surrounding sequence. CDK1 consensus is underlined. WD40 domains (51–90, 93–133, 135–175) are highlighted in dark grey. B, C WB of immunoprecipitated proteins following Nocodazole treatment, with mouse immunoglobulins used as control (IP ctr): B Endogenous proteins immunoprecipitated with anti-AMBRA1 antibody. C Overexpressed MYC-AMBRA1 immunoprecipitated using anti-MYC antibody. D WB of HeLa cells treated with Nocodazole and then with 9 μM RO-3306, in the last 10 min of treatment. The white arrow indicates AMBRA1 electrophoretic migration, while the black arrow indicates its mobility shift. AMBRA1 hypershift was visualized with a low percentage acrylamide gel (5–6%). E Autoradiography (32P signal) and WB of an in vitro kinase assay with recombinant CDK1/Cyclin B1 performed on MYC-AMBRA1 WT or AA1209/1223 and MYC-β-Galactosidase (βGal) as control. Proteins were immunoprecipitated using anti-MYC antibody following HeLa cells transfection with the relative constructs. An asterisk marks a MYC-AMBRA1 degradation sub-product. Gel percentages are indicated in each WB panel
