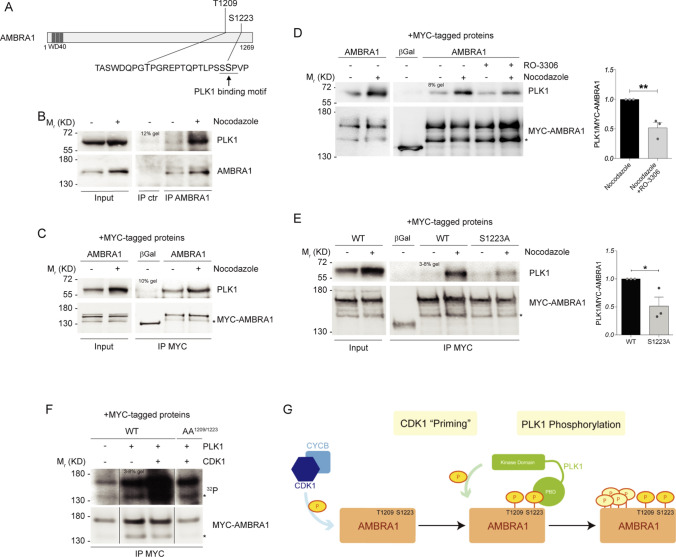
Fig. 3.
CDK1-mediated phosphorylation primes PLK1 phosphorylation on AMBRA1. A Schematic representation of AMBRA1 protein, highlighting T1209 and S1223 with their respective surrounding sequence. PLK1 binding motif is underlined. WD40 domains (51–90, 93–133, 135–175) are highlighted in dark grey. B–E WB of immunoprecipitated proteins following Nocodazole treatment: B Endogenous proteins were immunoprecipitated with AMBRA1 antibody. Mouse immunoglobulins were used as control (IP ctr). C–E Overexpressed MYC-AMBRA1 and MYC-β-Galactosidase as control immunoprecipitated using anti-MYC antibody. D HeLa cells treated in the last 10 min of Nocodazole with 9 μM RO-3306. E HeLa cells transfected with MYC-AMBRA1 WT or S1223 phosphosilent mutant (S1223A, Alanine substitution). Quantification, only for mitotic protein extracts, as mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments is shown, and significance is **(p < 0.005) for D and *(p < 0.05) for E, by Student’s T test. F Autoradiography (32P signal) and WB of an in vitro kinase assay with recombinant CDK1/Cyclin B1 and PLK1 performed on MYC-AMBRA1 WT or AA1209/1223 and MYC-β-Galactosidase (βGal) as control. Proteins were immunoprecipitated using anti-MYC antibody following HeLa cells transfection with the relative constructs. The image represented here derives from the same experiment in which lanes in the middle were cropped. G Model for AMBRA1 phosphorylation at mitosis: AMBRA1 is at first phosphorylated by CDK1/Cyclin B1 on T1209 and S1223, then pS1223 is bound by PLK1 that further phosphorylate AMBRA1 on additional sites. An asterisk marks a MYC-AMBRA1 degradation sub-product. Gel percentages are indicated in each WB panel