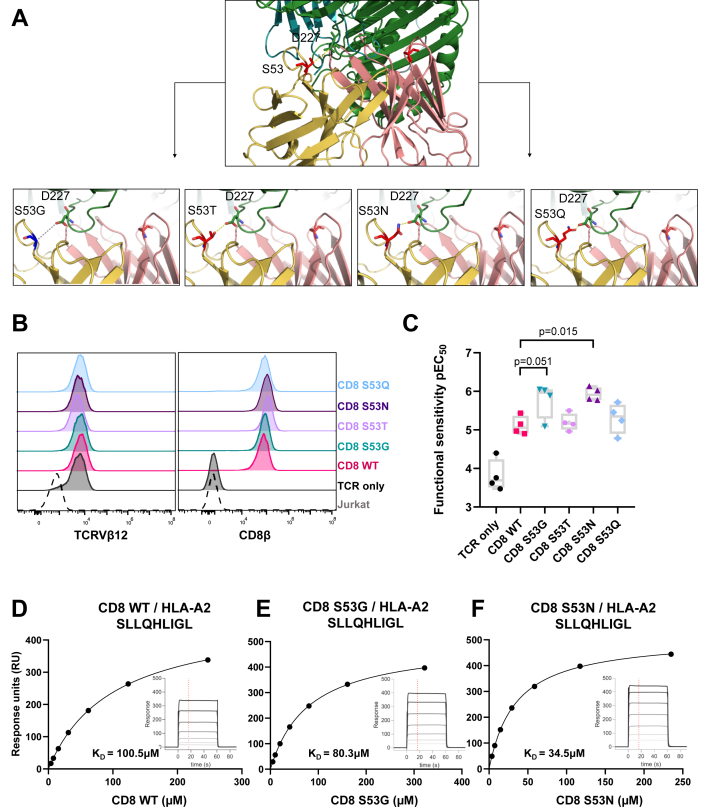
Figure 1.
Design and characterization of CD8 variants.A, crystal structure of human CD8αα complexed with HLA-A∗0201 (18) in cartoon form showing CD8α chain residue Ser53 (red) interacting with HLAα3 residue Asp227 (green). CD8α2 residue Ser53 mutations are shown in the four images below interacting with HLAα3 residue Asp227 (green). B, expression of TCRVβ12 and CD8β on Jurkat cells transduced with the RLA TCR and CD8αβ containing either wild-type (WT) CD8α or mutated forms (S53G, S53T, S53N, or S53Q) of CD8α. C, functional sensitivity of RLA TCR+ CD8αβ+ Jurkat cells expressed as the decimal cologarithm of the half-maximal efficacy concentration (pEC50). The activation of RLA TCR+ CD8αβ+ Jurkat cells in response to C1R HLA-A2 cells pulsed with serial dilutions of the cognate peptide was assessed by measuring the upregulation of CD69. Significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test to compare each variant versus wild-type CD8 (n = 4). Data are derived from four separate experiments. D–F, representative surface plasmon resonance affinity measurements of wild-type (WT) CD8αα (D) and the most functionally potent variants of CD8αα, namely S53G (E) and S53N (F), versus SLL/HLA-A∗0201.