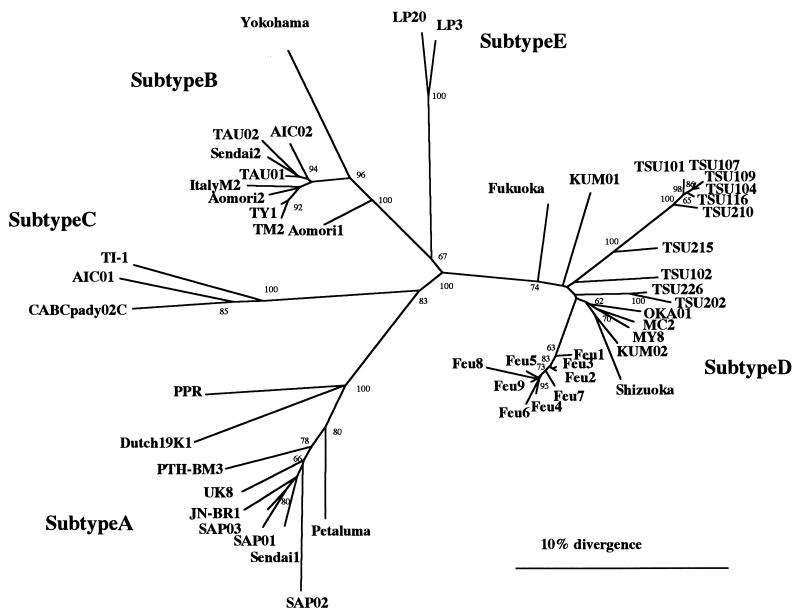
FIG. 2.
An unrooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of the FIV env gene covering variable regions V3 to V5. Nucleotide divergences were estimated by the DNADIST program from the PHYLIP software package (5). The phylogenic tree was constructed by using the NEIGHBOR program, and the branching order reliability was evaluated by bootstrap analysis in the SEQBOOT program (5). Virus clones obtained in this study are Feu1 to -9 from the Tsushima cat and TSU101, TSU102, TSU104, TSU107, TSU109, TSU116, TSU202, TSU210, TSU215, and TSU226 from domestic cats on Tsushima Island. The FIV clones previously reported are Petaluma FIV14 (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. M25381), TM2 (M59418), Yokohama (D37812), Shizuoka (D37811), JN-BR1 (D67052), MC2 (D67062), MY8 (D67063), TY1 (D67064), Sendai1 (D37813), Sendai2 (D37814), Aomori1 (D37816), Aomori2 (D37817), Fukuoka (D37815), PPR (M36968), UK8 (X69496), Dutch19k1 (M73964), ItalyM2 (X69501), LP3 (D84496), LP20 (D84498), TI-1, CABCpady02C (U02392), SAP01 (AB010402), SAP02 (AB010403), SAP03 (AB010404), PTH-BM3 (AB010401), TAU01 (AB10405), TAU02 (AB10406), AIC01 (AB10396), AIC02 (AB10397), OKA01 (AB010400), KUM01 (AB010398), and KUM02 (AB010399). The numbers at each branch point indicate the bootstrap values (5) preserved through greater than 60 in 100 bootstrap repetitions.