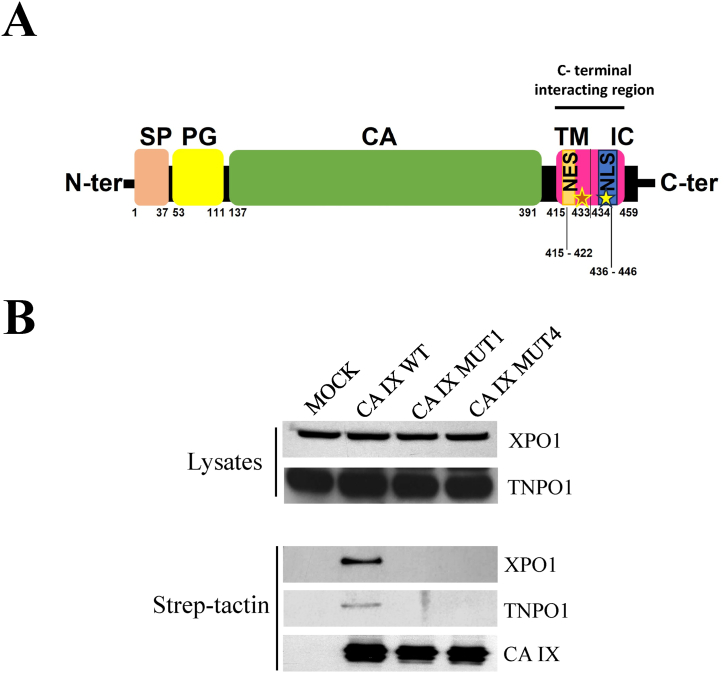
Fig. 1.
Co-precipitation analysis of wild-type and mutant CA IX proteins with components of the nucleocytoplasmic transport. A) Schematic representation of CA IX structural features and protein domains in its canonical transmembrane topology. From the N- to the C-terminus: Signal peptide (pink), a.a. 1–37; PG (proteoglycan) domain (yellow), a.a. 53–111; CA (catalytic) domain (green), a.a. 137–391; transmembrane (TM) and intracytosolic (IC) domains (lilac), a.a. 415–459. The asterisks in the C-terminal interacting region, encompassing the putative nuclear export signal (NES) and nuclear localization signal (NLS) denote the mutated sites of MUT1 and MUT 4 proteins used in this study. B) Western blot analysis of HEK-293 lysates expressing mock, CA IX WT, MUT1 (Leu423/Arg-Thr427/Arg), MUT4 (Arg436/Glu-Arg441/Glu), with XPO1 and TNPO1. Co-precipitation analysis of CA IX WT and its mutant proteins with XPO1 and TNPO1 after purification with strep-tactin resin. Uncropped images of the western blots are available as supplementary material (Succoio_supplementary_materials).