Fig. 2.
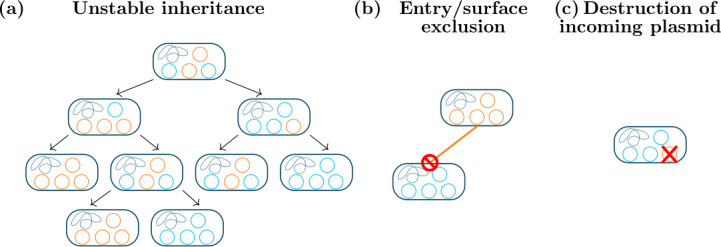
Mechanisms limiting coinfection of bacteria by multiple plasmids. (a) Unstable inheritance. Because the two plasmid types share a common copy number, random segregation at host cell division eventually ensures that they are separated into distinct hosts carrying only one plasmid type. (b) Surface and entry exclusion. The plasmids encode proteins which prevent the host cell from being a recipient in conjugation. (c) Destruction of the incoming plasmid. Novel plasmids are degraded by plasmid-encoded immune systems, such as CRISPR/Cas* or restriction enzymes* once in the host cell.
