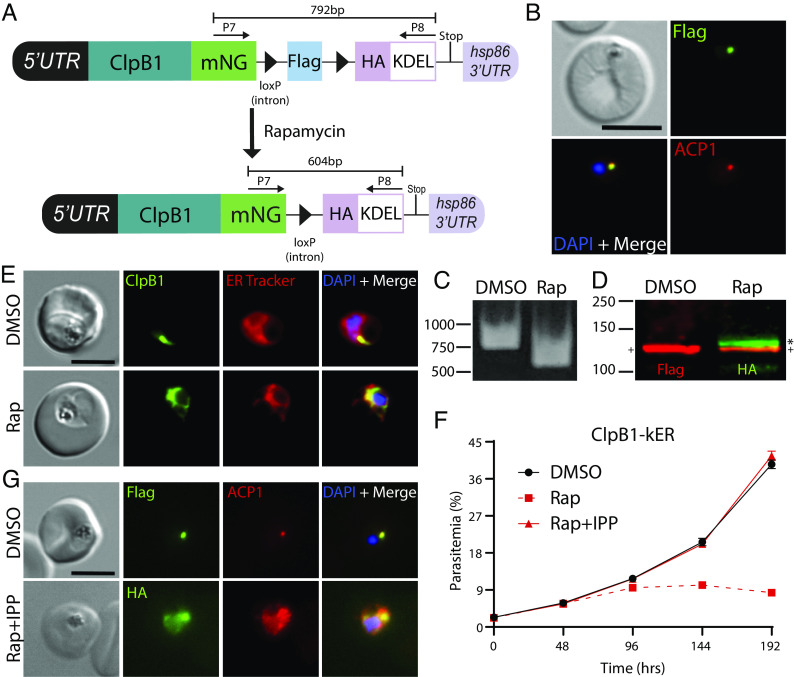
Fig. 2.
Lethal ER retention of the apicoplast chaperone ClpB1 is rescued by IPP. (A) Schematic showing strategy for appending kER to the C-terminus of clpB1. (B) IFA of PFA fixed parasites stained with mouse anti-Flag and rabbit anti-ACP1 antibodies. (C) PCR showing excision in ClpB1-kER parasites 24 h after rapamycin treatment using primers P7/8. (D) Western blot 24 h posttreatment with DMSO or rapamycin. Molecular weights after transit peptide cleavage are predicted to be 135 kDa for ClpB1-mNG-3xFLAG and 135.1 kDa for ClpB1-mNG-3xHA-KDEL. (+) represents the mature form of ClpB1 while the (*) represents ClpB1 with the transit peptide still attached. (E) Live microscopy of DMSO- or rapamycin-treated parasites 48 h posttreatment. (F) Representative growth of asynchronous parasites (n = 3 biological replicates) treated with DMSO or rapamycin, with or without supplementation with 200 µM IPP. Data are presented as means ± SD from one biological replicate (n = 3 technical replicates). (G) IFA of PFA fixed parasites stained with mouse anti-Flag or anti-HA and rabbit anti-ACP1 antibodies after three growth cycles where rapamycin-treated parasites were supplemented with 200 µM IPP. (Scale bars, 5 μm.)