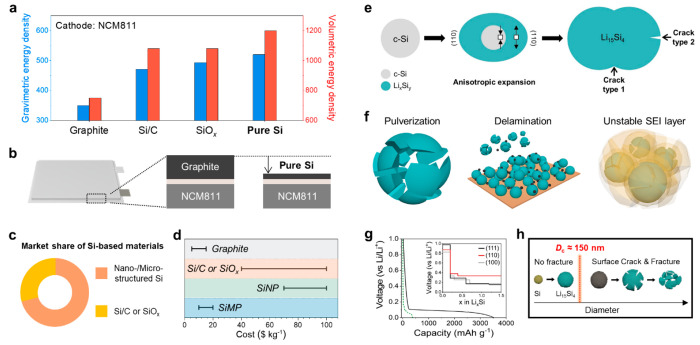
Figure 1.
Basic characteristics of the pure Si anode. (a) Practical gravimetric and volumetric energy densities of graphite, Si/C, SiOx, and pure Si anodes paired with the NCM811 cathode at the cell level (unit: Wh kg–1 and Wh L–1 for gravimetric energy density and volumetric energy density, respectively.) (b) Comparison of the cell thickness between graphite|NCM811 and pure Si|NCM811. (c) Current market share of Si-based materials and (d) cost comparison of graphite, Si/C or SiOx, pure SiNP, and pure SiMP. (e) Schematic diagram for volumetric expansion, the anisotropic property, and crack formation of crystalline Si during the lithiation process. (f) Main degradation mechanism of Si anodes originates from the large volume expansion of Si during lithiation. (g) Electrochemical lithiation curves of Si (black solid line) and graphite (green dashed line) anodes (inset: DFT voltage profiles for the lithiated reaction into each (111), (110), and (111) plane of crystalline Si). Adapted with permission from ref (15). Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society. (h) Critical size (Dc) for occurring particle fracture upon lithiation and volume expansion.