FIG 3.
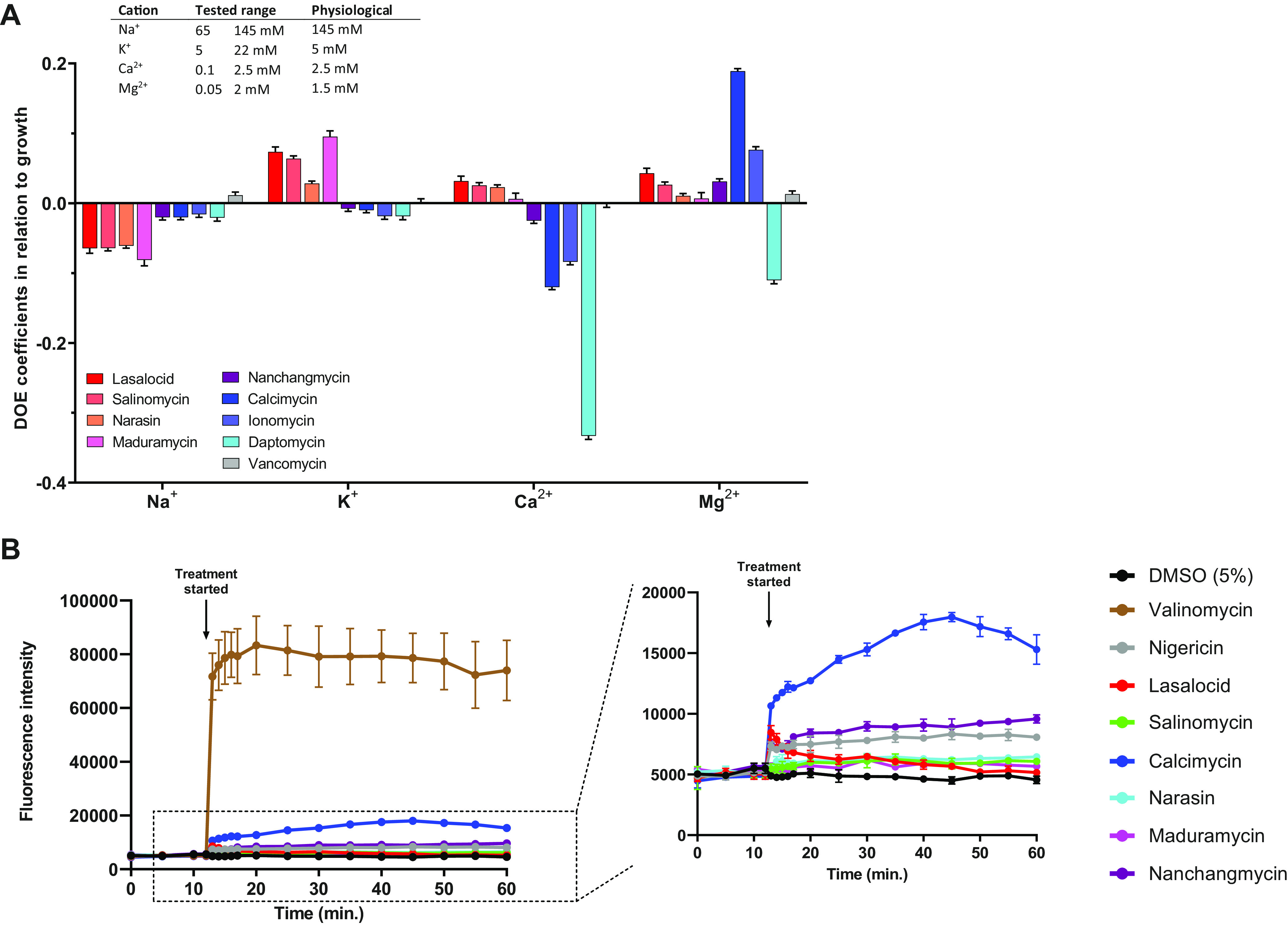
Cation dependency of polyether ionophores. (A) A full factorial design of experiment (DOE)-approach was used to study how ionophore activity depends on cation concentrations (Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+). The concentrations of the four cations were chosen as factors, and the percentage change in growth compared to a control as the response. S. aureus was treated with the compounds at 0.25× MIC (1× MIC for daptomycin) in the presence of cations in the concentration ranges listed in the figure. Bacterial growth was evaluated after overnight treatment, and MODDE Pro was used for data processing. Daptomycin and vancomycin were included as positive and negative controls, respectively. Results are average of technical triplicates. (B) Ionophore effects on membrane potential were studied using the membrane-potential sensitive dye 3,3-dipropylthiacarbocyanine iodide [DiSC3(5)]. S. aureus was loaded with 1 μM DiSC3(5) (1%), and after the dye had stabilized, the culture was treated with 10× MIC (CM-M9 medium). Valinomycin (20 μg/mL) and nigericin (10 μg/mL) were included as positive and negative controls, respectively. Results are average of technical triplicates (distinct wells), and bars are means ± SD (standard deviation) (n = 3).
