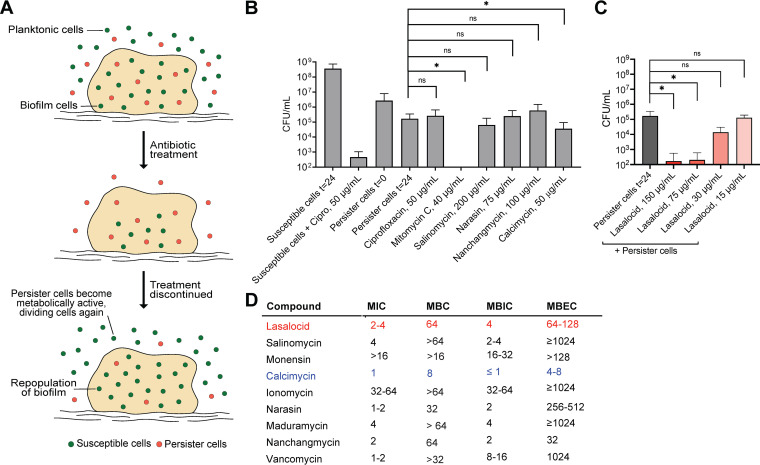
FIG 4.
Polyether ionophore action on S. aureus persister cells and biofilms. (A) Illustration showing the lack of antibiotic effect against persister and biofilm cells. (B) Persister cell killing with 50× MIC (the respective concentrations are listed in the figure). Persister cells were produced by transferring growing, susceptible bacteria into a modified CM-M9 medium without available carbon sources. Persister cells reverted to susceptible cells when transferred into a nutrient-rich medium (susceptible cells t = 24). Ciprofloxacin (50 μg/mL) and mitomycin C (40 μg/mL) were included as negative and positive controls, respectively. Bars are mean ± SD (n = 9). (C) Persister cell killing with lasalocid at 5×, 10×, 25×, and 50× MIC. Bars are means ± SD (n = 9). (D) Biofilm inhibition and eradication. A S. aureus biofilm was grown for 24 h before antibiotic treatment. Minimum biofilm inhibition concentration (MBIC) was determined after 24 h of treatment, and minimum biofilm eradication concentration (MBEC) was determined after 72 h of biofilm recovery. Lasalocid (red) and calcimycin (blue) are highlighted for clarity. All results shown are averages of biological triplicates, each with technical triplicates.