Fig. 6.
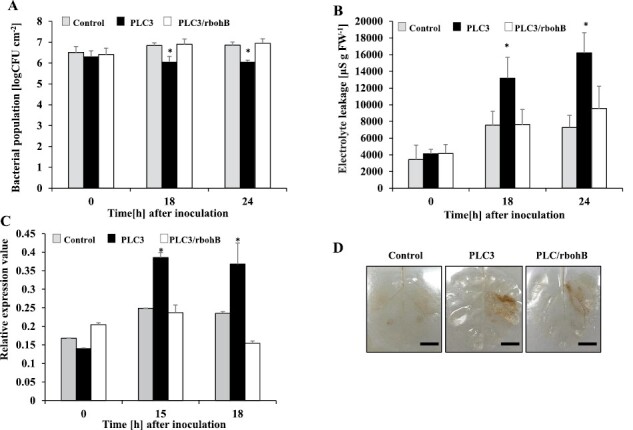
Role of reactive oxygen species in accelerated HR in NbPLC3s-silenced plants. Empty vector control, NbPLC3s (PLC3), and NbPLC3s:NbrbohB double-knockdown (PLC3/rbohB) plant leaves were infiltrated with R. solanacearum 8107. (A) Bacterial populations were determined in control, PLC3, and PLC3/rbohB plants by plating at 0, 18, and 24 h following inoculation. Values are means ±SD of four replicate experiments. Asterisks show significant differences among control, PLC3, and PLC3/rbohB plants (P<0.05, t-test). (B) Cell death induction was determined at 0, 18, and 24 h by measuring the ion conductivity levels in the control, PLC3s, and PLC3s/rbohB plants. Values are means ±SD of four replicate experiments. Asterisks show significant differences among control, PLC3, and PLC3/rbohB plants (P<0.05, t-test). (C) Total RNA was isolated from control, NbPLC3s (PLC3), and NbPLC3s:NbrbohB double-knockdown (PLC3/rbohB) plants at 0, 15, and 18 h after inoculation with R. solanacearum 8107. Expression values of Nbhin1 are shown as relative expression after normalization to internal standard genes (NbUbe35/NbNQO). Values represent means ±SD from triplicate experiments. Asterisks denote values significantly different from those of control plants (*; P<0.05, t-test). (D) ROS production was seen 18 h after inoculation as assessed by DAB staining. These experiments were repeated with 10 biological replicates, and representative results are shown. Scale bars=1 cm.
