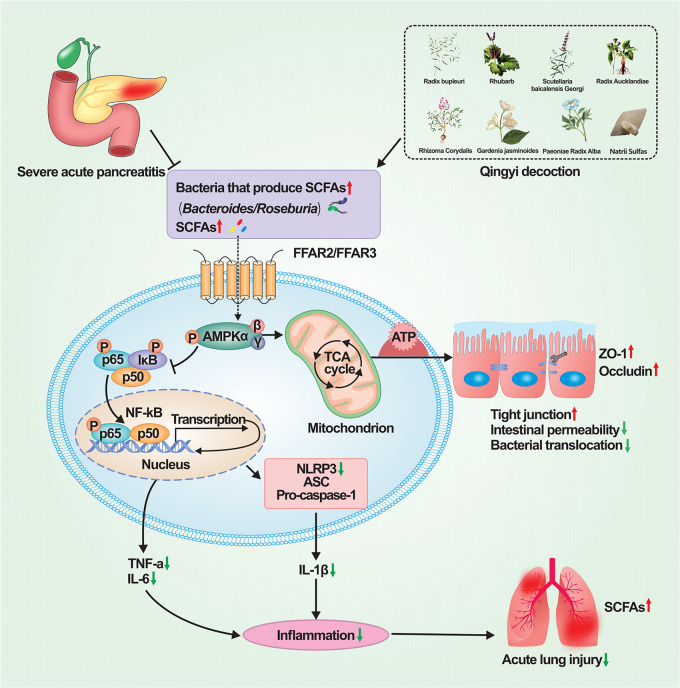
FIG 8.
Mechanisms of Qingyi decoction in alleviating SAP-ALI via gut microbiota, which is probably associated with short-chain fatty acids-mediated AMPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. QYD treatment increased the relative abundance of SCFAs-producing bacteria, which would lead to a relative increase in the production of SCFAs. Combining SCFAs with G protein-coupled receptors in intestine and lungs cells can cause phosphorylation of AMPK, thereby inhibiting the expression of downstream target proteins NF-κB and NLRP3, and ultimately reducing histopathological damage and strengthening the intestinal barrier function, inhibiting the systemic sustained proinflammatory response to relieve SAP-ALI. AMPK, AMP (AMP)-activated protein kinase; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein; ATP, adenosine 5′-triphosphate; FFAR, free fatty acid receptor; IκB, inhibitors of kappaB; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; P, phosphorylation; p50, NF-kappa B1; p65, NF-kappa B RelA; SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; SAP-ALI, severe acute pancreatitis associated acute lung injury; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1.