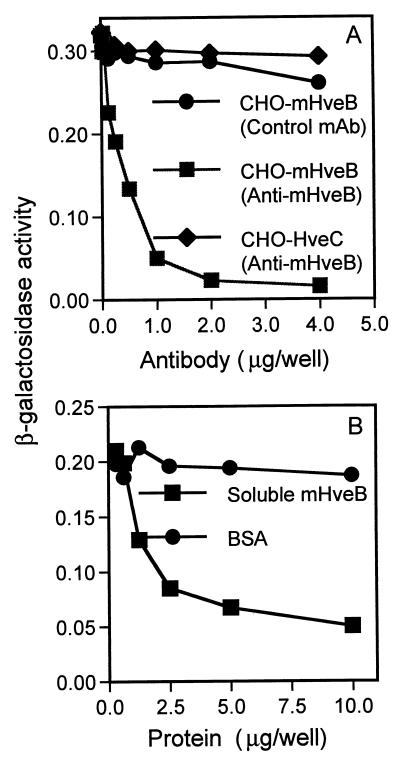
FIG. 2.
Anti-mHveB MAb and soluble mHveB blocked entry of PRV into mHveB-expressing CHO-K1 cells. The CHO cells were transiently transfected in six-well dishes with mHveB-expressing pDS6 (squares and circles) and human HveC-expressing pBG38 (12) (diamonds) with Lipofectamine (Gibco-BRL). At 24 h posttransfection, the cells were replated in 96-well tissue culture dishes. The following day, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and inoculated with PRV. (A) The cells were incubated for 30 min with serial dilutions of purified anti-mHveB MAb 6B3 (squares and diamonds) or control anti-myc MAb (circles), and then a constant dose of β-galactosidase-expressing PRV (106 PFU/well) was added. After 3 h of incubation, the virus-MAb mixtures were removed, unpenetrated virus was inactivated by brief treatment with 100 mM citrate buffer (pH 3.0), and incubation was continued for another 3 h. The cells were permeabilized, and ONPG (o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside) substrate was added for quantitation of β-galactosidase activity at 405 nm with a Dynatech enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader or a Spectromax 250 reader. (B) Purified soluble mHveB protein (squares) or BSA (circles) at amounts indicated was added to 5 × 105 PFU of β-galactosidase-expressing PRV and incubated for 30 min. Soluble protein-virus mixtures were added to mHveB-expressing CHO-K1 cells plated in 96-well dishes. Three hours postinfection, residual virus was neutralized by treatment of cells with 100 mM citrate, pH 3.0. Medium was replenished, and 4 h later, viral entry was assayed as described above.