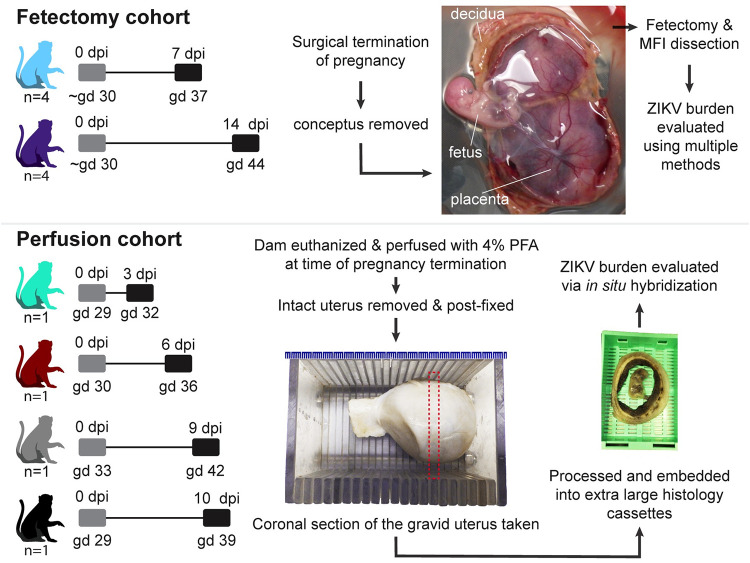
Fig 1. Experimental design.
The pathway to vertical transmission was evaluated using two cohorts of pregnant rhesus macaques. The fetectomy cohort consisted of a total of eight dams that were inoculated with ZIKV-DAK at gestational day (gd) 30. These pregnancies were surgically terminated (four at 7 days post infection (dpi) and four at 14 dpi), the conceptus was removed and a fetectomy and maternal-fetal interface (MFI) dissection was performed to collect specimens that were evaluated for ZIKV burden using multiple methods. The gross image of the fetus shows the fetus, the placenta (with the chorionic plate facing up) and the relatively thick decidua which is seen curled around at the edges of the placental discs. The perfusion cohort consisted of four dams that were inoculated with ZIKV-DAK at gd 30. At the time of pregnancy termination (either 3, 6, 9, or 10 dpi), the dams underwent terminal perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), and the gravid uterus was collected. The post-fixed uterus was sliced using a slicing box, creating consistent coronal sections of the entire uterus. Dashed line depicts a coronal section. These coronal sections were routinely processed and paraffin embedded using extra-large histology cassettes and viral burden in the coronal sections was evaluated using in situ hybridization. Gray boxes indicate the day of inoculation and black boxes indicate pregnancy termination.