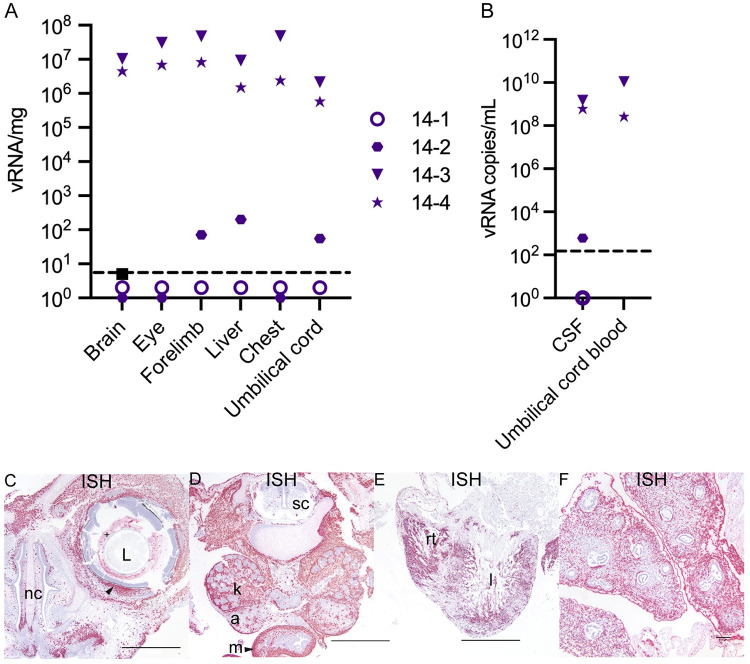
Fig 8. ZIKV burden in the fetus at 14 dpi.
(A) ZIKV RNA detected in fetal tissues and organs. The limit of detection of 3 copies/mg is depicted by the dashed line. (B) ZIKV RNA detected in fetal fluids. The limit of detection of 150 copies/mL is depicted by the dashed line. CSF = cerebrospinal fluid. (C)–(E) ZIKV RNA detected via ISH (pink). (C)(D) images from 14–3 and (E)(F) from 14–4. (C)–(F) Scale bars represent 1000 μm. (C) Infection detected in the eye of the fetus with ZIKV (+) in the material (vitreous/aqueous humor) surrounding the lens (L) and within the sclera of the eye indicated by the arrow. ZIKV was also detected subjacent to the nasal mucosa of the fetal nasal cavity (nc). (D) ZIKV RNA detected in the kidneys (k), adrenal glands (a), and intestinal muscular layers (m) with minimal scattered positivity in the spinal cord (sc). (E) Abundant ZIKV was detected throughout the myocardium of the right (rt) and left (l) ventricles of the heart and (F) in the pulmonary interstitium of the lungs with sparing of the respiratory epithelium of the bronchi and bronchioles. Scale bar represents 100 μm.