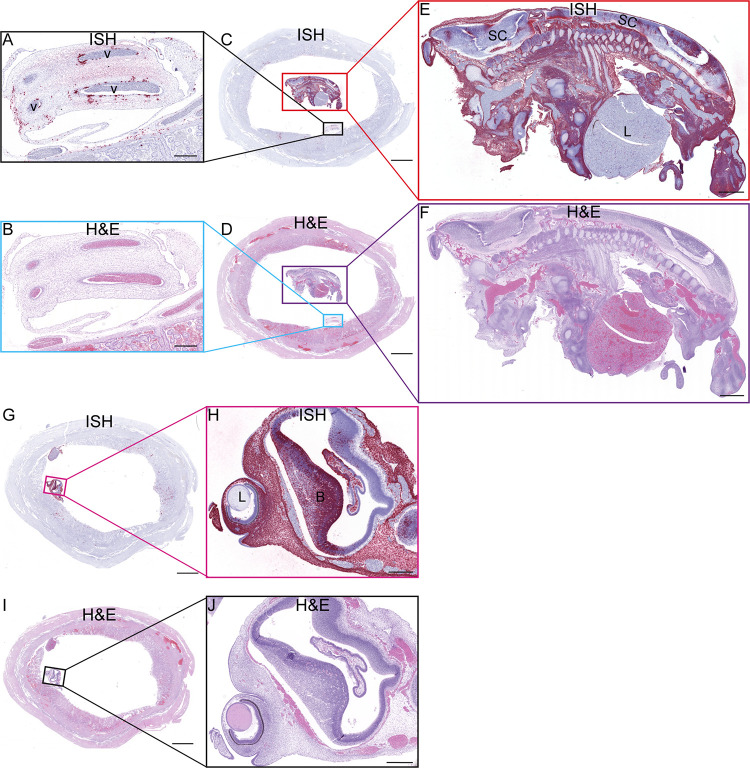
Fig 14. ZIKV RNA detected at 10 dpi via ISH.
(A) ISH staining for ZIKV (pink) in the endothelial lining of the umbilical vessels (v) and multifocally scattered throughout Wharton’s jelly surrounding the affected vessels of the umbilical cord. (B) Corresponding H&E stained section. (C) Full slide evaluated for ZIKV RNA via ISH. The black square outlines the area magnified in (A) and the red square is magnified in (E). (D) The corresponding H&E stained section shown in (C). The area outlined in blue is magnified in (B) and the area outlined in purple is magnified in (F). (E) ZIKV RNA detected in the body of the fetus via ISH (pink). There is marked diffuse ZIKV RNA (pink) in the majority of tissues with less intense and single cell positivity in the spinal cord (SC) and liver (L). ZIKV RNA was not detected in the cartilage and immature bone of the skeleton of the fetus. (F) The corresponding H&E stained section of the sample shown in (E). (G) Full slide evaluated for ZIKV RNA via ISH. The pink square outlines the portion of the slide magnified in (H). (H) The head of the fetus with ZIKV RNA identified via ISH (pink) in the sclera of the eye (arrow), brain (B), and tissues of head. ZIKV RNA was not found in the lens (L) of the eye. (I) (J) Corresponding H&E stained section of specimens shown in (G) and (I), respectively. (A)(B)(H)(J) Scale bars represent 500 μm. (C)(D)(G)(I) The scale bars represent 5000 μm. (E)(F) The scale bars represent 1000 μm.