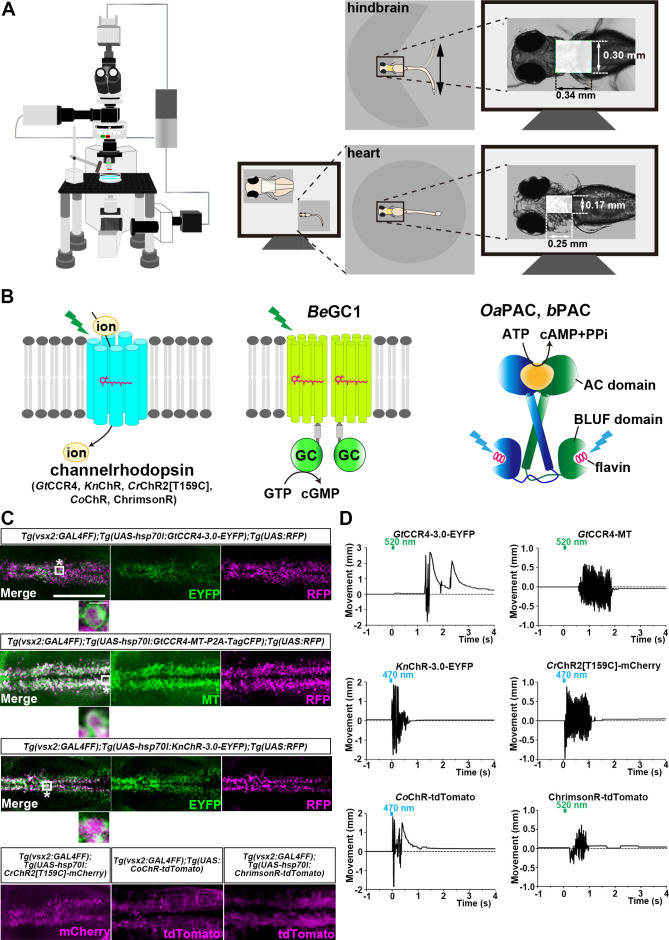
Figure 2. Optogenetic activation of hindbrain reticulospinal V2a neurons and cardiomyocytes by channelrhodopsins.
(A) Schematic of experimental devices. A larva was embedded in agarose. The hindbrain region or the heart were irradiated with light. Tail (caudal fin) movements and heartbeats were monitored by a high-speed camera with infrared light. (B) Schematic diagram of optogenetic tools used in this study. GC, guanylyl cyclase; AC, adenylyl cyclase; BLUF, sensors of blue-light using FAD. (C) Expression of GtCCR4-3.0-EYFP, GtCCR4-MT, KnChR-3.0-EYFP, CrChR2[T159C]-mCherry, CoChR-tdTomato, and ChrimsonR-tdTomato in the zebrafish hindbrain reticulospinal V2a neurons. 3 dpf (day post fertilization) Tg(vsx2:GAL4FF);Tg(UAS-hsp70l:GtCCR4-3.0-EYFP, GtCCR4-MT-P2A-TagCFP, KnChR-3.0-EYFP, or CrChR2[T159C]-mCherry, myl7:mCherry) larvae were fixed and stained with anti-GFP (EYFP, green), anti-Myc tag (green) or anti-DsRed (RFP, magenta) antibodies. For CoChR and ChrimsonR, fluorescent images of the hindbrain of Tg(vsx2:GAL4FF);Tg(UAS:CoChR-tdTomato, or UAS-hsp70l:ChrimsonR-tdTomato, myl7:mCherry) larvae are shown. Inset: higher magnification images for the boxed areas showing double-labeled neurons. (D) Tail movements of 3-dpf Tg larvae expressing GtCCR4-3.0-EYFP, GtCCR4-MT, KnChR-3.0-EYFP, and CrChR2[T159C]-mCherry, CoChR-tdTomato, and ChrimsonR-tdTomato in the reticulospinal V2a neurons after stimulation of the hindbrain area with LED (0.4 mW/mm2) light with a wavelength of 520 nm (GtCCR4-3.0-EYFP, GtCCR4-MT, ChrimsonR-tdTomato) and 470 nm (KnChR-3.0-EYFP, CrChR2[T159C]-mCherry, CoChR-tdTomato) for 100 ms. Light stimulations started at time 0 s. Typical examples are shown. Scale bars = 150 μm in (C), 5 μm in the insets of (C).