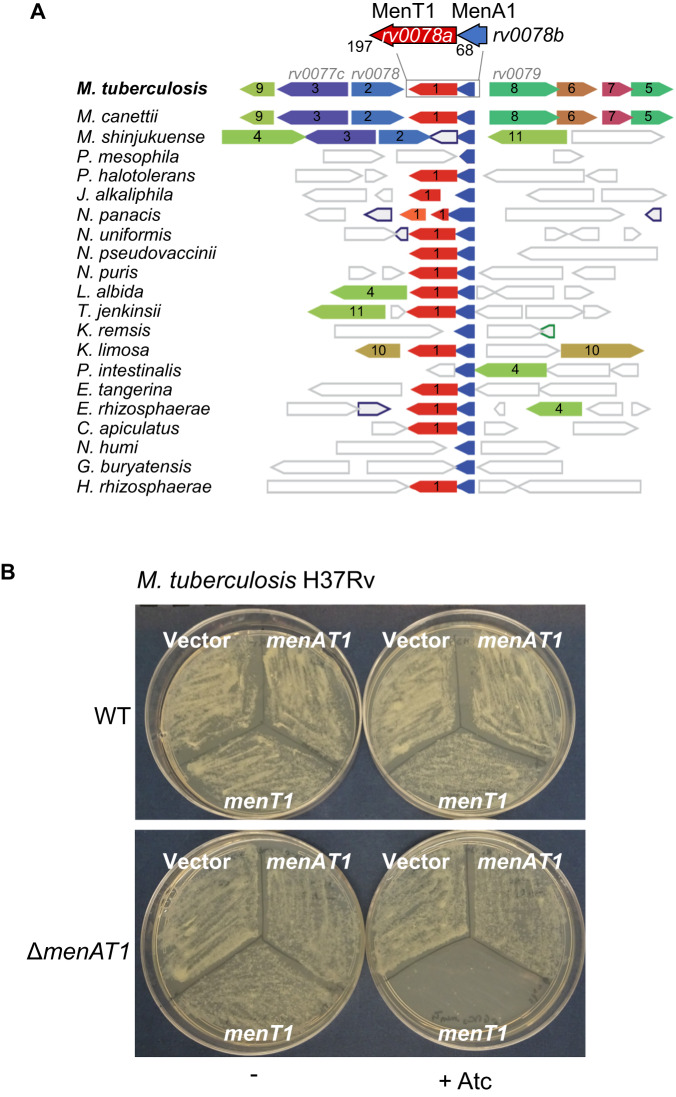
Fig. 1. MenAT1 is a bona fide TA system in M. tuberculosis.
A Conservation of gene neighbourhoods and maximum likelihood phylogenetic analyses were used to study the distribution of menA1 genes (performed with FlaGs, http://www.webflags.se/). The menA1 gene is highlighted in blue, and non-conserved genes are not coloured. The genes encoding proteins that belong to a homologous cluster in more than one genomic neighbourhood are indicated by colour (refer to supplementary datasheet 1 for the identification of clusters and their corresponding flanking protein accession numbers). Among the most conserved adjacent proteins, (2) corresponds to Rv0078 a known repressor of menTA1, (3) to Rv0077c a putative oxidoreductase, (8) to Rv0079 unknown gene of the dormancy regulon, (11) to a putative LysR transcription regulator, (4) to a P-loop-NTPase containing domain, and (10) to a rifampin ADP-ribosyltransferase. Full names of bacterial species are given in Fig. S1. B M. tuberculosis H37Rv or its mutant strain Δ(menA1-menT1)::ZeoR was transformed with pGMC vector, pGMC-menT1, or pGMC-menAT1. Following phenotypic expression, half of the transformation mix was plated on 7H11 OADC plates with Sm, and the other half was plated on 7H11 OADC Sm plates that were supplemented with 200 ng.ml−1 of Atc inducer. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 20 days. The data presented are representative of three independent experiments.