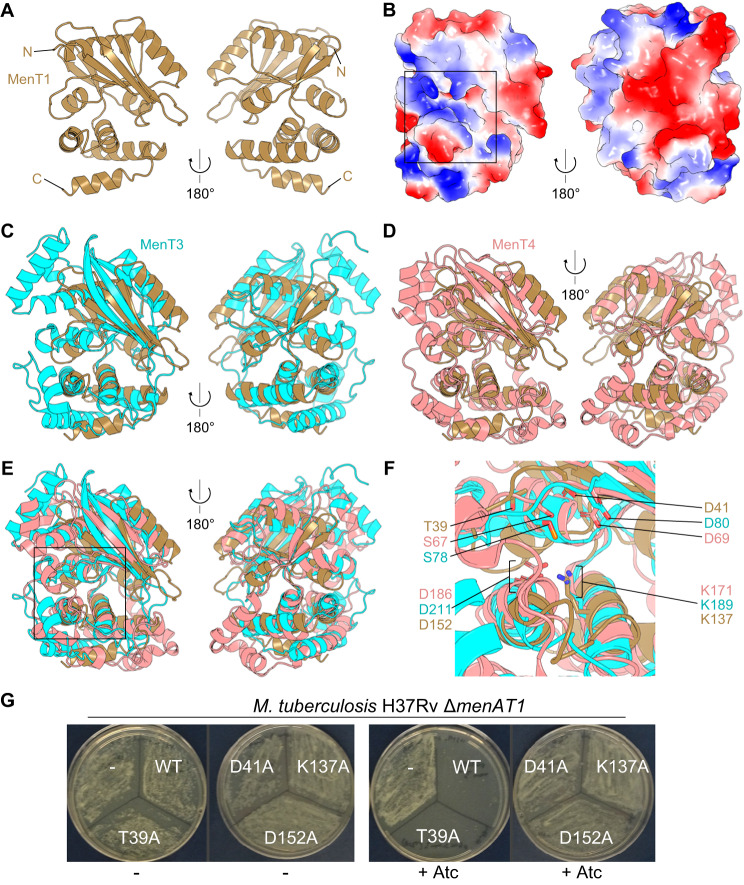
Fig. 2. MenT toxins have conserved folds and catalytic sites.
A Structure of monomeric MenT1 toxin, with views from front and back, shown as cartoons coloured “sand”. N and C termini are indicated. B Surface electrostatics of MenT1, viewed as in (A), with red for electronegative and blue for electropositive potential. Electrostatics were generated using default settings for the APBS plugin (PyMol). The box indicates likely site of catalysis. C Superposition of MenT1 and MenT3 (cyan cartoon), viewed as per (A). D Superposition of MenT1 and MenT4 (salmon cartoon), viewed as per (A). E Superposition of MenT1, MenT3 and MenT4, viewed as per (A). F Close-up view of boxed region in (E), highlighting MenT toxin active site residues. G A toxicity assay was performed to evaluate the potential activity centre of MenT1 in M. tuberculosis. The mutant strain Δ(menA1-menT1)::ZeoR was transformed with 100 ng plasmids expressing either MenT1 WT or mutant alleles T39A, D41A, K137A, or D152A. Following phenotypic expression, half of the transformation mix was plated on 7H11 OADC plates with Sm, and the other half was plated on 7H11 OADC Sm plates that were supplemented with 200 ng.ml−1 of Atc. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 20 days. The data presented are representative of three independent experiments.