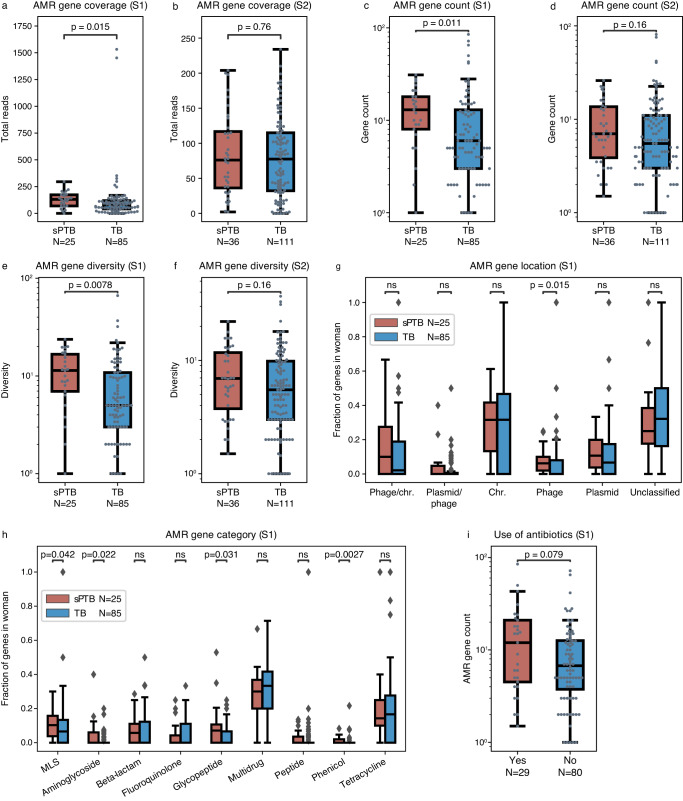
Fig. 4. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) gene profiles of the vaginal microbiome are associated with sPTB.
a, b Total subsampled reads (105) mapped to AMR genes compared between sPTB and TB, in the first (S1, a) and second (S2, b) halves of pregnancy. c, d Median count (along period) of AMR genes compared between sPTB and TB, in the first (S1, c) and second (S2, d) halves of pregnancy. e, f Median Shannon-Wiener diversity (along period) of AMR genes compared between sPTB and TB, in the first (S1, e) and second (S2, f) halves of pregnancy. g Fraction of AMR genes originating in different locations, shown as median along the first half of each pregnancy. Chr.: chromosome. h Fraction of AMR genes belonging to different resistance categories, shown as median along the first half of each pregnancy. MLS, macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin B. i AMR gene richness in the first half of pregnancy (S1) compared between women who used and did not use antibiotics in the 6 months before pregnancy. Box, IQR; line, median; whiskers, 1.5*IQR; p, two-sided Mann-Whitney U.