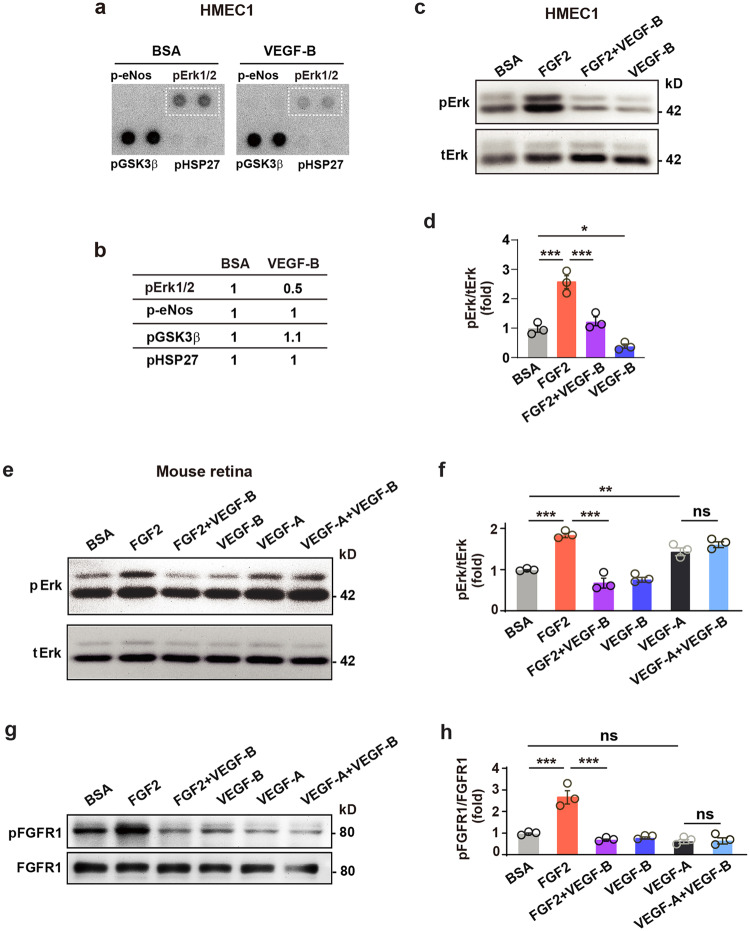
Fig. 3.
VEGF-B inhibits FGF2-induced Erk activation in vitro and in vivo. a, b Images of phospho-kinase antibody array screening (a) using HMEC1s and corresponding quantifications (b). c, d Western blots showing that VEGF-B (100 ng/ml, 10 min treatment) reduced FGF2 (50 ng/ml)-induced Erk phosphorylation in HMEC1. One-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc analysis was used (number of comparisons, 3). Adjusted p values are 2.1E−4 for BSA vs FGF2; 4.0E−4 for FGF2 vs FGF2 + VEGF-B, and 0.021 for VEGF-B vs BSA. e, f Western blots showing that in mouse retinae, intravitreal injection of VEGF-B inhibited FGF2-, but not VEGF-A-induced Erk phosphorylation (30 min after injection). Adjusted p values are 1.1E−5 for BSA vs FGF2; 1.5E−7 for FGF2 vs FGF2 + VEGF-B; 2.7E−3 for VEGF-A vs BSA and 0.14 for VEGF-A vs VEGF-A + VEGF-B. g, h Western blots showing that in mouse retinae, intravitreal injection of VEGF-B inhibited FGF2-induced FGFR1 phosphorylation (30 min after injection). Adjusted p values are 8.2E−6 for BSA vs FGF2; 5.5E−7 for FGF2 vs FGF2 + VEGF-B and 0.85 for VEGF-A vs VEGF-A + VEGF-B. For (f) and (h), two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak post hoc analysis was used (number of comparisons, 9). n = 3 each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns: p > 0.05. The experiments were repeated three times