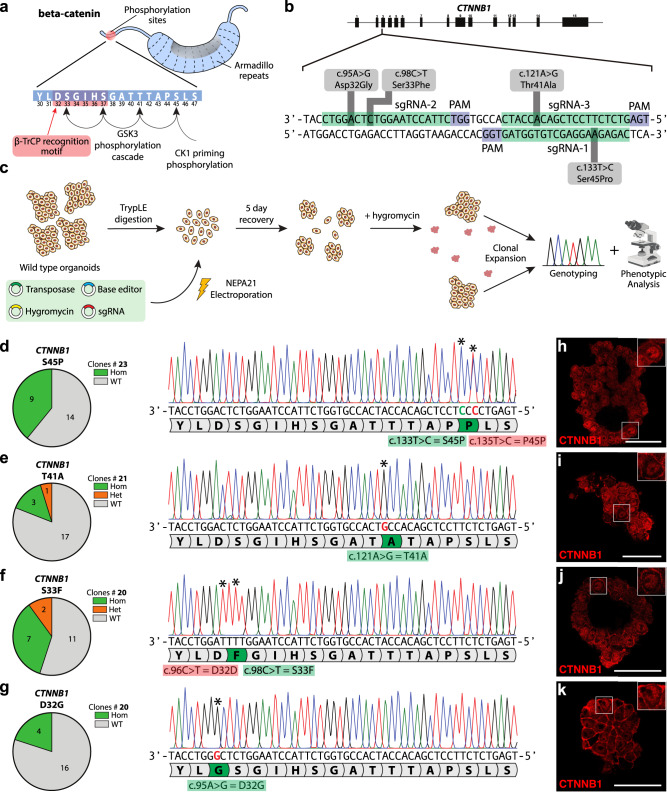
Fig. 1. Introduction of oncogenic activation mutations in CTNNB1 in hepatocyte organoids using conventional and evolved CBE and ABE.
a Protein encoded by the gene CTNNB1 harbors hot-spot mutations in the N-terminus, which correlate with principles of CTNNB1 degradation by kinases CK1 and GSK3 followed by proteasomal destruction by E3-ligase β-TrCP. b Design of 3 sgRNA’s for introduction of hot-spot mutations in exon 3 of CTNNB1. sgRNA-1 can be used with SpCas9-ABE to introduce priming kinase mutation S45P, sgRNA-2 can be used with SpCas9-ABE to introduce D32G or with SpCas9-CBE to introduce S33F and sgRNA-3 in combination with SpCas9-NG-ABE introduces T41A. sgRNA sequences are in green, PAM sequences are in blue. c Principles of hepatocyte organoid electroporation for CTNNB1 mutagenesis. d–g Sanger trace and quantification of editing efficiency by Sanger sequencing of hygromycin-resistant organoids harboring CTNNB1S45P (d), CTNNB1T41A (e), CTNNB1S33F (f), and CTNNB1-D32G (g). Asterisks highlight mutated nucleotides. Correct mutations are highlighted in green and synonymous but unintended mutations are highlighted in red. h–k CBE and ABE mutated hepatocyte organoids on residue S45 (h), T41 (i), S33 (j), and D32 (k) show increased intracellular localization of CTNNB1. Scale bar in (h–k) is 50 µm. Source data are provided as a Source data file.