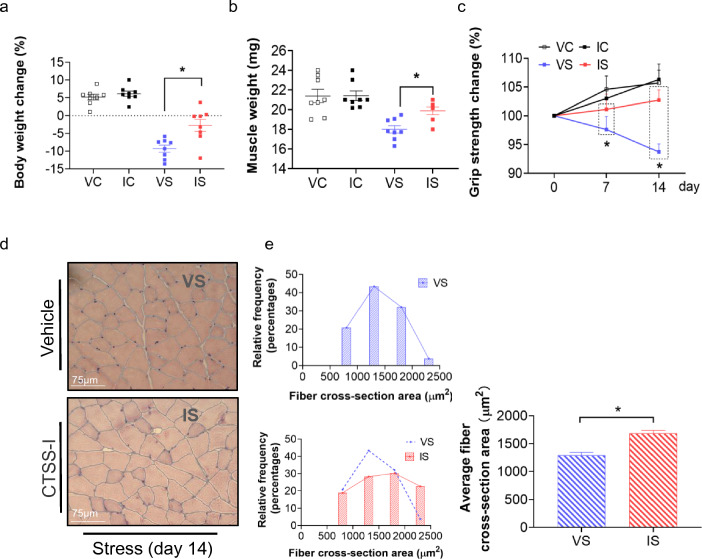
Fig. 6.
The cathepsin S inhibitor (CTSS-I) alleviated stress-related skeletal muscle injury and dysfunction. a, b: The body weights and GAS muscle weights of the four groups of mice (n = 8, each group). c: The measurements of all four limbs’ grip strength in four groups of mice at the indicated time points (n = 8 each). d, e: Representative H&E images and quantitative data for the cross sections of GAS muscle fibers harvested from the four groups of mice on Day 14. Scale bar: 75 µm. The data are mean ± SEM, and p-values were determined by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc tests (a, b), unpaired Student’s t test (E right panel), or two-way repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc tests (c). VC: CTSS+/+ loaded vehicle + non-stress, IC: CTSS+/+ loaded CTSS-I + non-stress, VS: CTSS+/+ loaded vehicle + stress, IS: CTSS+/+ loaded CTSS-I + stress. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; N.S, not significant