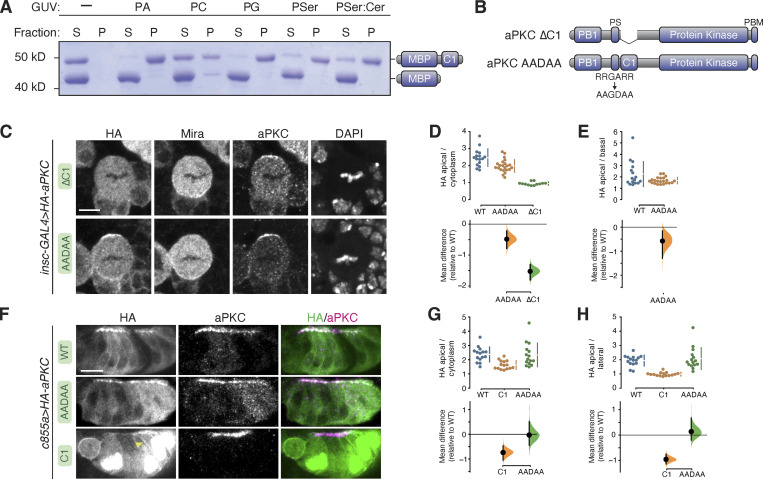
Figure 5.
Phospholipid binding of aPKC C1 domain and role of C1 and PS domains in aPKC localization in larval brain NSCs and epithelia. (A) Binding of a maltose binding protein (MBP) fusion of the aPKC C1 domain to phospholipids. Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions from cosedimentation with Giant Unilamellar Vesicles (GUVs) of the indicated phospholipid composition are shown (PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidyl choline; PG, phosphatidyl glycerol; PSer, phosphatidyl serine; PSer:Cer, phosphatidyl serine mixture with ceramide). MBP alone is included as an internal negative control. (B) Schematics of ∆C1 and AADAA aPKC variants. (C) Localization of HA-tagged aPKC ∆C1 and AADAA variants in metaphase larval brain NSCs. The basal marker Miranda, total aPKC (expressed variant and endogenous), and nucleic acids (DAPI) are shown for comparison. The scale bar is 5 µm. (D and E) Gardner–Altman estimation plots of aPKC AADAA and ∆C1 cortical localization in NSCs. Apical cortical to cytoplasmic (D) or apical to basal (E) signal intensity ratios of anti-HA signals are shown for individual metaphase NSCs expressing either aPKC AADAA or ∆C1. The data for wild type is the same as in Fig. 1. Apical to basal ratios are only shown for proteins with detectable membrane signals. Error bar in the upper graphs represents one standard deviation (gap is mean); error bar in the lower graphs represents bootstrap 95% confidence interval; n = 16 (from six distinct larval brains), 22 (8), and 12 (5) for WT, AADAA, and ∆C1, respectively. (F) Localization of HA-tagged aPKC ∆C1 and AADAA variants in larval brain inner proliferation center (IPC) epithelium. Arrowhead highlights aPKC C1 localization at the lateral membrane. As in interphase NSC cells, the C1 is highly enriched in the epithelial nuclei. Scale bar is 5 µm. (G and H) Gardner–Altman estimation plots of aPKC AADAA and C1 cortical localization in IPC epithelial cells. Apical cortical to cytoplasmic (D) or apical to lateral (E) signal intensity ratios of anti-HA signals are shown for individual epithelial cells from the IPC expressing either aPKC AADAA or C1. Error bar in upper graphs represents one standard deviation (gap is mean); error bar in lower graphs represents bootstrap 95% confidence interval; n = 16 (from three distinct larval brains), 15 (3), and 15 (3) for WT, C1, and AADAA, respectively. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F5.