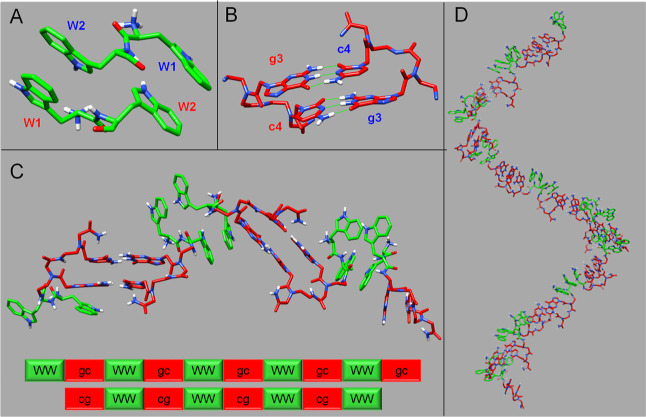
Figure 6.
3D structural model of a WWgc helical bilayer. (A) Dimeric WW structural arrangement obtained by docking calculations. Tryptophan sequence numbers are indicated, and different colors are used for W belonging to different chains of the dimer. (B) gc Watson-Crick canonical base pairing in adjacent WWgc units. H-bonds are reported with green lines. (C) Assembly of a WWgc tetramer. The aggregates are stabilized by π–π aromatic interactions in between tryptophan side chains in two facing monomers, whose backbones run in an antiparallel manner, and by canonical Watson-Crick gc/cg base pairing. (D) Right-handed helical bilayer made up of 19 WWgc units. Fibers could be generated by side-by-side association of several bilayers. In all figures, tryptophan residues are colored in green and PNA bases in red.