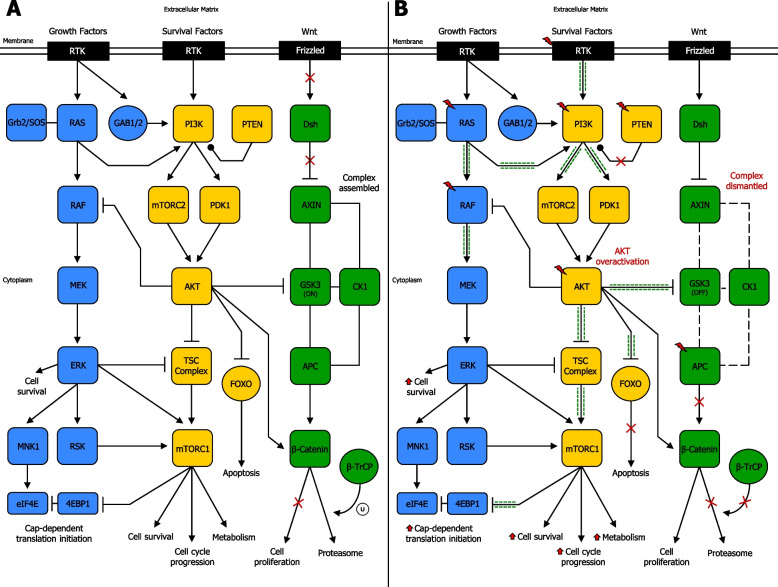
Fig. 7.
Network of signaling cross-regulation between PAM pathway and RAS/ERK pathway or Wnt/GSK3/β-catenin pathway. A Simplified cross-regulation between PAM pathway and RAS/ERK pathway or Wnt/GSK3/β-catenin pathway in normal cells. Numerous cross-talk points occur between PAM pathway and RAS/ERK pathway or Wnt/GSK3/β-catenin pathway, leading to ordinary cell survival and proliferation, cell cycle progression, cell metabolism, apoptosis, and other cellular functions. B Simplified cross-regulation between PAM pathway and RAS/ERK pathway or Wnt/GSK3/β-catenin pathway in cancer cells. Mutations in RTK, RAS, PI3K, PTEN, AKT, APC, and possibly other genes, may occur, resulting in cross-talk dysregulations between PAM pathway and RAS/ERK pathway or Wnt/GSK3/β-catenin pathway. This can lead to enhanced PAM downstream signaling, such as increased cell survival and proliferation, enhanced cell cycle progression, boosted cell metabolism, reduced apoptosis, and dysregulation of other important cellular functions. Activation (phosphorylation or non-phosphorylation) is shown with arrowhead lines, inhibition (phosphorylation or non-phosphorylation) is indicated with blocked lines, interaction is displayed with continuous lines, disassociation is shown with dotted lines, and dephosphorylation, carried out by phosphatases, is indicated with roundhead lines. Red lightning symbol shows mutation for a particular gene in the PAM pathway. Red crosses emphasise signaling blockage, whereas green dash-dotted lines (adjacent to arrowhead lines or blocked lines) highlight signaling enhancement. Red upper-arrows show increases. U: ubiquitination