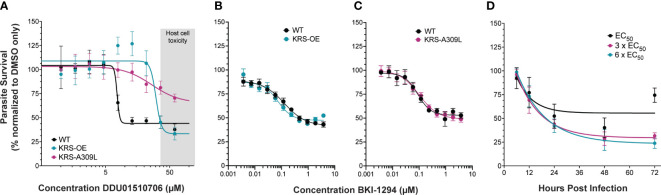
Figure 3.
Genetic validation that KRS inhibitors are on-target. (A) Overexpression of CpKRS (KRS-OE, teal) or mutation of CpKRS with an A309L substitution (KRS-A309L, magenta) render parasites less susceptible to treatment with DDD01510706 compared to wild type parasites (WT, black). WT parasites used for drug assays are a transgenic reporter strain that expresses NanoLuciferase and are WT for CpKRS (Supplemental Figure 2C). Host toxicity indicated in grey (see Supplemental Figure 5). (B, C) Drug mode of action is specific to inhibition of CpKRS. KRS-OE and KRS-A309L are equally susceptible as WT parasites to treatment with compounds that inhibit a non-CpKRS target (BKI-1294 an inhibitor of CpCDPK1). Mean ± SEM; 4 biological replicates, each with 4 technical replicates. (D) WT parasites were cultured in vitro with DDD01510706 at the EC50 (7.5 µM, black), 3 x EC50 (22.5 µM, magenta), or 6 x EC50 (45 µM, teal) to determine the rate-of-kill. Compound was added at the time of infection, and parasite survival was measured by NanoLuciferase at the indicated timepoints post infection. Treatment with DDD01510706 reduces parasite growth within 24 hours post-infection, corresponding to peak CpKRS expression. One phase decay linear regression plotted (GraphPad). Mean ± SD; representative graph of three biological replicates, each with 3 technical replicates. Curves were analyzed by extra-sum-of-squares F test, where the null hypothesis (one curve fits both datasets) is rejected if p<0.05. Figure 1A: WT vs OE-KRS p<0.0001; WT vs A309L-KRS p<0.0001. Figures 1B, C: WT vs OE-KRS p=0.1148; WT vs A309L-KRS p=0.8501