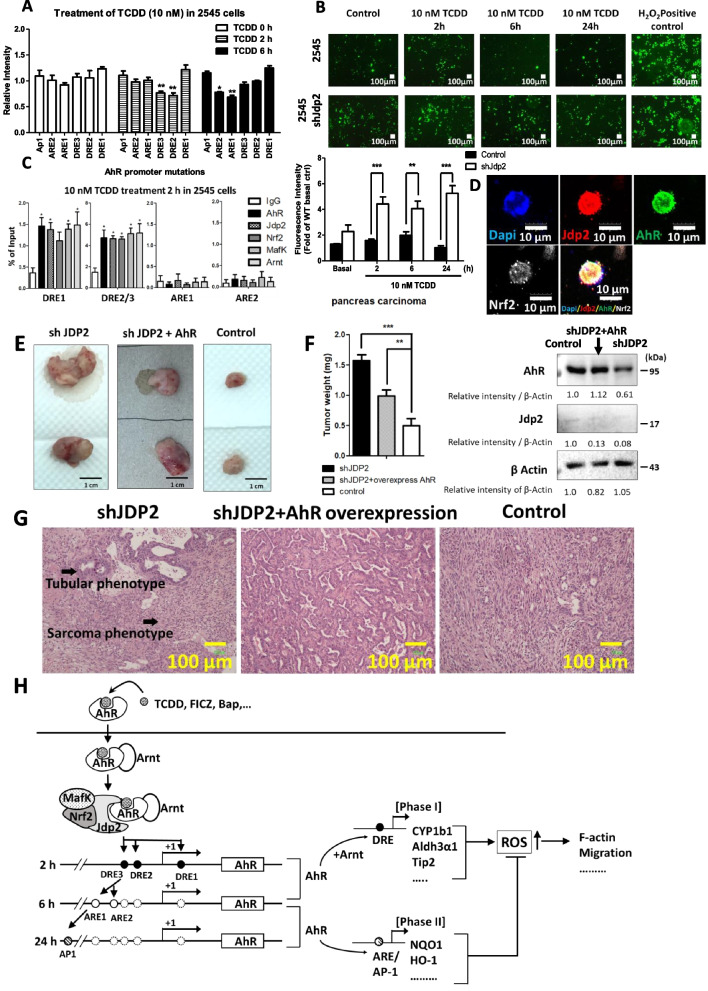
Fig. 7.
Rescue of tumorigenesis by overexpression of AhR in shJdp2-treated Kras-Trp53-mutated pancreatic carcinoma 2545 cells. A–C The role of the Jdp2–AhR axis in pancreatic cancer 2545 cells was examined in response to TCDD using AhR luciferase, ROS generation, and ChIP assays. A Effects of the mutation of each cis-element, ARE1, ARE2, DRE1, DRE2, and DRE3, on the AhR promoter region. Luciferase activity was measured in 2545 cells in the presence of 10 nM TCDD at indicated time-periods, as described in the “Methods” section. The luciferase activity of full-length (FL) AhR luciferase was arbitrarily set at 1.0. Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test (*p < 0.05). B ROS activity was measured in 2545 cells in response to exposure to 10 nM TCDD for indicted time-periods. ROS production was detected using CM-H2DCFDA, as described in the “Methods” section. Representative fluorescence images of ROS generation in 2545 cells (top) and 2545 cells treated with shJdp2-treated 2545 cells (bottom) are shown. The data obtained in the fluorescence images of ROS levels detected using CM-H2DCFDA after treatment with TCDD were analyzed using ImageJ software. The fluorescence intensity of 2545 cells without TCDD was set at 1.0. Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). C ChIP assay of the AhR–Jdp2–Nrf2 axis. Regions amplified by PCR with the specific corresponding primers (ARE1, ARE2, and DRE1) and with the primers that contained the DRE2 and DRE3 cis-elements as indicated in WT MEFs. ChIP–qPCR analyses were performed using chromatin extracts from 2545 cells stimulated with TCDD for 2 h with the indicated antibodies and normal IgG (as a negative control). The probes for ARE1, ARE2, DRE1, and DRE2/3 were used in the presence of 10 nM TCDD. Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test (*p < 0.05). D Coimmunostaining of AhR–Nrf2–Jdp2 protein complexes in 2545 tumor cells. 2545 cells were stained with rabbit anti-Jdp2 (a gift from A. Aronheim), rat anti-Nrf2 (Cell Signaling Technology), and goat anti-AhR (Santa Cruz Co.); with Alexa-Fluor® 488 conjugated Rabbit anti-Goat IgG (Thermo Fisher Scientific), Alexa Fluor® 594-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and Alexa Fluor® 647-labeled goat anti-rat IgG (H + L) (Cell Signal Technology). The cells were stained by 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), to detect cell nuclei (Sigma-Aldrich). Scale bars, 10 μm. E Xenograft transplantation of mouse 2546 pancreatic cancers, Jdp2-knockdown cells, and AhR-forced-expressed Jdp2-knockdown 2546 cells was performed as described in the “Methods” section. Xenotransplantation and tumor formation assays were performed as described previously [36]. 2546 pancreatic tumor cells (1 × 106 cells) and the transfectants by CSIV-CMV-AhR-IRES2-Venus virus were cultured for 2 days, and 1 × 105 cells were inoculated into SCID mice as described previously [30]. F Tumor weight was calculated in three replicates. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc multiple-comparison test. The expression of AhR and Jdp2 cropped figures are shown. See Supplementary Figure S8 for the original full-length blot images. The intensity of each band was then quantified. The relative value was normalized to β-Actin and shown as ratio. G Representative results for tumor biopsies stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The region labeled with an arrowhead indicates a different carcinoma phenotype. The characteristics of each treatment are shown for following phenotypes: shJdp2 treatment produced a large area of necrosis, more epithelial–mesenchymal transition phenotypes, and the sarcoma phenotype; shJdp2 + AhR overexpression produced a smaller area of necrosis and mainly the epithelial phenotype; the control produced results like those produced by shJdp2 treatment and smaller areas of necrosis. H Schematic representation of DMSO-induced AhR activation through the complexes of AhR-Jdp2, Nrf2-Jdp2, and AhR-Nrf2 to increase ROS production, cell spreading, and apoptosis in WT MEFs. In Jdp2−/− MEFs, only a residual amount of AhR‒Arnt was recruited to the DRE2 and DRE3 elements of the AhR promoter