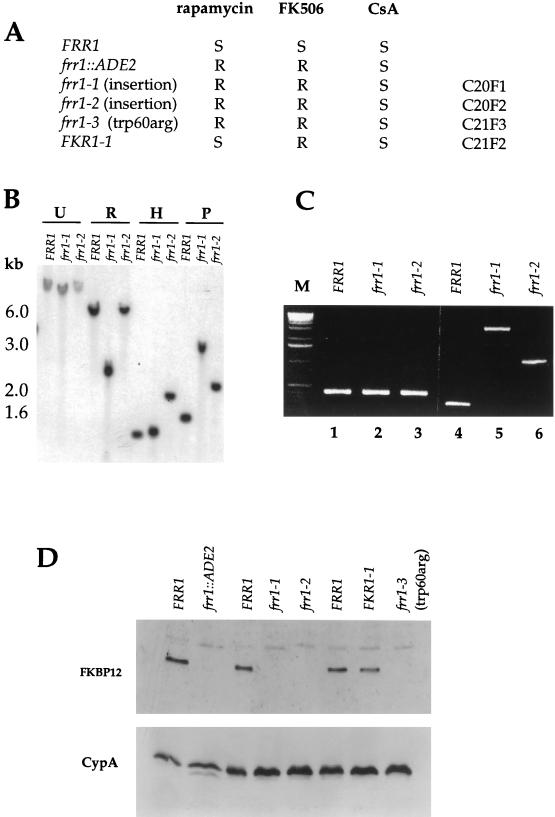
FIG. 6.
Spontaneous frr1 mutations confer rapamycin and FK506 resistance in C. neoformans. (A) FRR1 wild-type (H99, JEC20, and JEC21) and isogenic frr1::ADE2, frr1-1, frr1-2, frr1-3, and FKR1-1 mutant strains were grown on YPD medium containing rapamycin (1 μg/ml), FK506 (1 μg/ml), or CsA (100 μg/ml). R and S, drug resistant and sensitive, respectively. (B) Southern analysis of genomic DNA from isogenic wild-type FRR1 and frr1 rapamycin-FK506-resistant mutant strains. Genomic DNA was cleaved with EcoRI (R), HindIII (H), or PstI (P), electrophoresed in a 0.8% agarose gel, transferred to nitrocellulose, and hybridized to a 700-bp FRR1 gene probe. Positions of DNA size markers are shown on the left. (C) PCR amplification of the frr1 mutant locus in strains C20F1, C20F2, and C21F3. Genomic DNA was PCR amplified with a pair of primers directed against the N-terminal region of the FKBP12 gene (primers 1 and 2) or against the C-terminal region of the FKBP12 gene (primers 3 and 4). The longer PCR products in lanes 5 and 6 resulting from strains C20F1 and C20F2 were cloned and sequenced, revealing novel DNA sequences of ∼2,200 and ∼780 bp that have inserted into the FKBP12 locus in strains C20F1 and C20F2 and are flanked by FKBP12 gene sequence in both cases. Lane M, markers. (D) Rapamycin-resistant mutants fail to express FKBP12. Protein extracts from wild-type and isogenic rapamycin-resistant mutants were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with rabbit polyclonal antiserum against yeast FKBP12. Strains were FRR1 wild-type serotype A strain H99 and the isogenic frr1::ADE2 mutant strain, wild-type FRR1 serotype D strain JEC20 and the isogenic frr1-1 (C20F1) and frr1-2 (C20F2) mutant strains, and wild-type FRR1 serotype D strain JEC21 and the isogenic FKR1-1 (C21F2) and frr1-3 (C21F3) mutant strains. One hundred micrograms of protein from the same extracts was analyzed by Western blotting with antiserum against the C. neoformans cyclophilin A protein (CypA) as a loading control.