Figure 3.
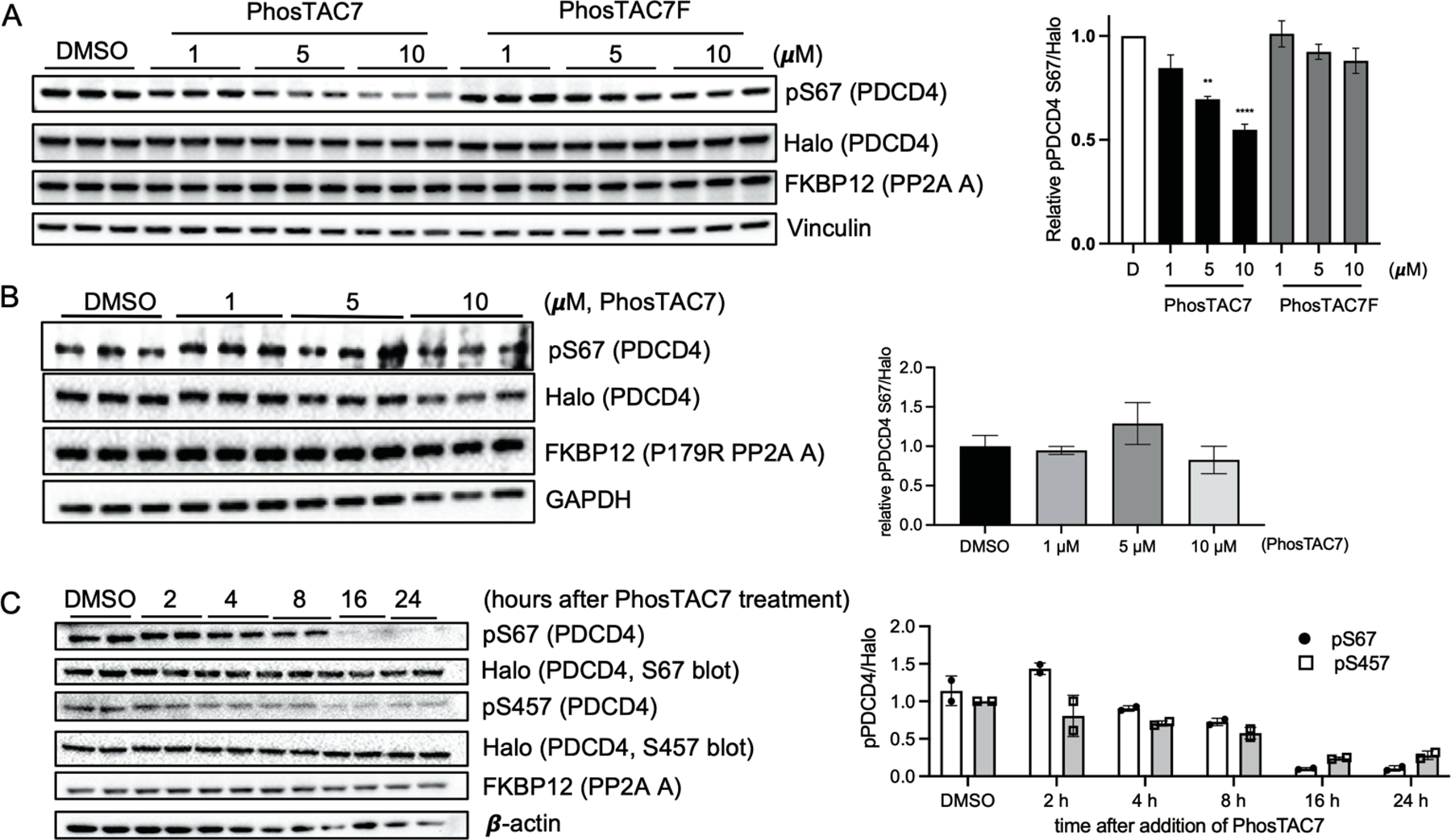
Recruitment of PP2A A subunit induces dephosphorylation of PDCD4. (a) PhosTAC7 but not inactive PhosTAC7F induces PDCD4 dephosphorylation at serine 67. Halo-PDCD4/FKBP12(F36V)-PP2A A wild type HeLa cells were treated with indicated concentrations of PhosTAC7, PhosTAC7F, or DMSO. Cell lysates were collected 12 h after treatment and analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. Data were quantified from three biological samples and summarized as mean and standard error of the mean. (**p= 0.0016, ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA) (b) PP2AA(P179R) mutant cannot induce PDCD4 dephosphorylation at serine 67. Halo-PDCD4/FKBP12(F36V)-PP2A A P179R mutant HeLa cells were treated with indicated concentrations of PhosTAC7 or DMSO. Cell lysates were collected 12 h after treatment and analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. Data were quantified from three biological replicates and summarized by their means and standard deviations. (c) Dephosphorylation kinetics of PDCD4 by PhosTAC7. Halo-PDCD4/FKBP12(F36V)-PP2A A wild type HeLa cells were treated with DMSO or PhosTAC7 (5 μM). Cell lysates were collected at indicated time points after treatment and analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. Data were quantified from two biological replicates and summarized as means and standard deviations.
