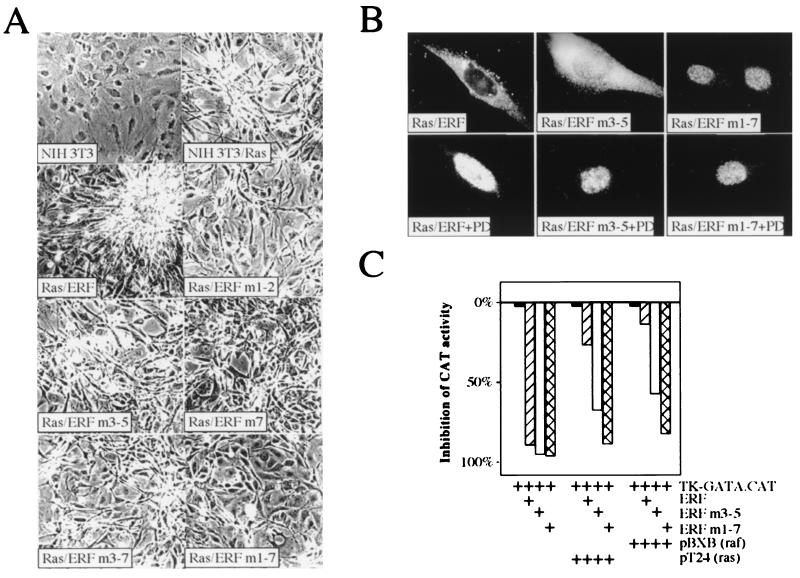
FIG. 7.
ERF mutants can suppress the ras-transformed phenotype. (A) NIH 3T3 cells transformed with pT24 Ha-ras were transfected with wt or phosphorylation-deficient ERF mutants. Transformed cells were selected with G418 to establish colonies and cell lines. Cells from established cell lines were grown in the presence of 1% serum for 10 days to determine effects on cell morphology and photographed with a 10× phase-contrast lens. The numbers indicate the mutation(s) for each plasmid: 1, T148A; 2, S161A; 3, S246A; 4, S251A; 5, T271A; 6, T357A, and 7, T526A. (B) The subcellular localization of ERF mutants in ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells was determined by immunofluorescence in exponentially growing cells in the presence or absence of the specific MEK1 inhibitor PD98059 (PD). (C) One microgram of the pTK-GATA.CAT reporter plasmid was cotransfected into HeLa cells with 0.5 μg of the indicated ERF plasmid and 1 μg of the indicated Ha-ras and c-raf-1 plasmids. The bars indicate inhibition of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) activity relative to that in the samples in the absence of exogenous ERF.