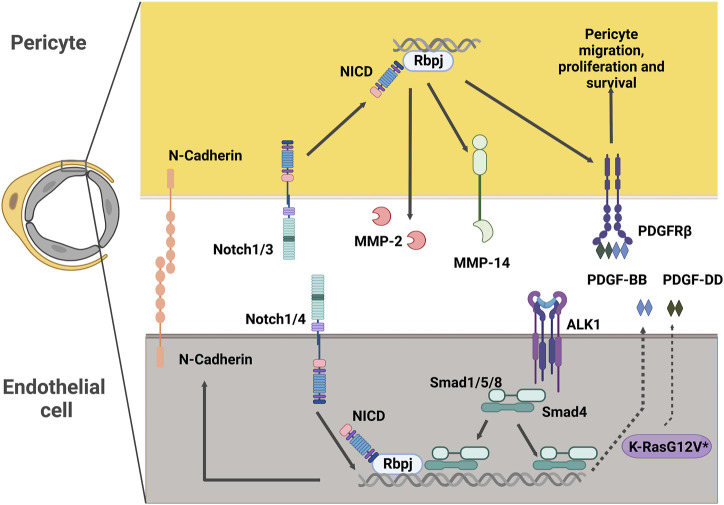
FIGURE 4.
Potential intercellular signaling between endothelial cells and pericytes in CNS AVMs. Notch signaling in pericytes promotes expression of MMP-14 and MMP-2, which are modulators of extracellular matrix structure. Notch signaling in pericytes also promotes expression of PDGFRβ, a key receptor driving essential pericyte functions such as migration, proliferation and survival. In endothelial cells, Notch intracellular domain can associate with Smad4 to regulate the levels of endothelial N-Cadherin. Alk1 signals in endothelial cells to promote the expression of PDGF-B. Expression of the pathogenic variant K-RasG12V in endothelial cells results in higher levels of PDGF-D. Both PDGF-B and PDGF-D function as ligands of the PDGFRβ present in mural cells. NICD: Notch Intracellular Domain, MMP: Matrix Metalloprotease, PDGFR: Platelet Derived Growth Factor Receptor, PDGF: Platelet Derived Growth Factor, ALK1: Activin receptor-like kinase 1, Rbpj: Recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J.