FIG. 9.
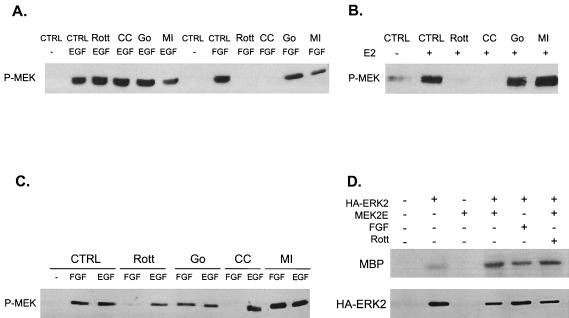
Activation of MEK but not ERK requires PKCδ. (A) PKCδ inhibitors block MEK activation by FGF but not EGF in H19-7 cells. Cells were either untreated (CTRL) or were pretreated with 1 μM Gö 6976 (Go) for 2 h, 5 μM rottlerin (Rott) for 6 h, 1 μM chelerythrine chloride (CC) for 2 h, or 30 μM MEK inhibitor PD98059 (MI) for 15 min. Cells were then stimulated with 10 ng of either FGF or EGF per ml for 10 min. After cell lysis, equal protein aliquots were resolved by SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide). MEK activation was assayed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-MEK (P-MEK) antibody. (B) PKCδ inhibitors block MEK activation by estradiol in ΔRaf-1:ER cells. Cells were pretreated as for panel A and then exposed to 1 μM estradiol for 30 min. Samples were resolved by SDS and assayed for MEK activation as for panel A. (C) PKCδ inhibitors block MEK activation by FGF but not EGF in PC12 cells. PC12 cells were treated and processed as for panel A. (D) Rottlerin does not block activation of ERK by constitutively activated MEK. H19-7 cells were mock transfected or cotransfected with an expression vector for HA-ERK2 and MEK-2E, a constitutively activated MEK. Cells were then left untreated or were pretreated with 5 μM rottlerin for 6 h or stimulated with 10 ng of FGF per ml as indicated. Following treatment, cells were lysed, and HA-ERK was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody. The immunoprecipitated HA-ERK was assayed for kinase activity by using MBP as a substrate as described in Materials and Methods, and the reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide). The immunoprecipitated ERK was quantitated by immunoblotting.