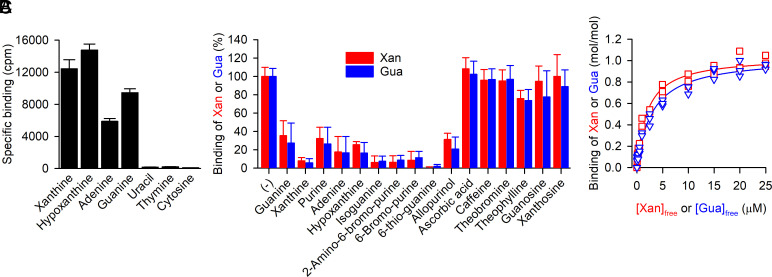
Fig. 1.
Substrate specificity of PurTCp. (A) Binding of 0.5 µM 3H-xanthine, 3H-hypoxanthine, 3H-adenine, 3H-guanine, 3H-uracil, 3H-thymine, or 3H-cytosine (all at a specific radioactivity of 5 Ci/mmol) was measured with the SPA using 100 ng of purified PurTCp in 200 mM Tris/MES, pH 7.0, 10% glycerol, 0.1 mM TCEP, and 0.1% decyl-β-D-maltopyranoside for 16 h at 4 °C. Specific binding was determined by subtracting the nonspecific counts per minute (cpm) determined in the presence of 800 mM imidazole, which competes with the PurTCp-His tag for binding to the Cu2+-His tag SPA beads, from the cpm measured in the absence of imidazole. (B) Binding of 0.5 µM 3H-xanthine (red) or 3H-guanine (blue) to 100 ng of purified PurTCp in the presence or absence of 250 µM of the indicated compound in assay buffer composed of 200 mM Tris/MES, pH 8.0, 20% (v/v) glycerol, 1 mM TCEP, and 0.1% DDM. Data were normalized to the cpm measured in the absence of compounds for 3H-xanthine or 3H-guanine binding. Data in panels A and B are the mean ± SEM of n ≥ 3 (each performed as a technical replicate). (C) Saturation binding of 3H-xanthine (red) or 3H-guanine (blue) to 100 ng of purified PurTCp was performed in the same buffer as used in the experiments shown in panel B and yielded a dissociation constant (Kd) for xanthine binding of 2.02 ± 0.2 µM and a Kd for guanine binding of 3.02 ± 0.33 µM with a molar substrate-to-PurTCp binding ratio of 1.04 ± 0.02 and 1.04 ± 0.03 for xanthine and guanine binding, respectively. Data of three independent experiments each performed in triplicate were subjected to global nonlinear regression fitting in Prism 8.