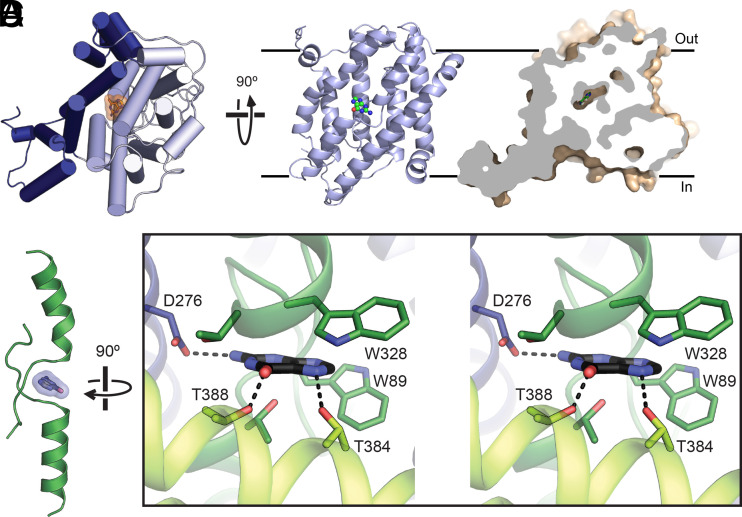
Fig. 3.
Substrate binding site. (A) A protomer of PurTCp viewed from the extracellular side (Left) and the transport domain viewed from the membrane (Right), with the bound substrate molecule. (B) Cutaway surface representation of a PurTCp monomer. (C) The bound substrate (blue) in PurTCp is shown in relation to the TM3 and TM10 transmembrane passes. (D) Stereo view of the substrate-binding site in PurTCp, with nearby residues shown as sticks and potential hydrogen bonds marked with dashed lines.