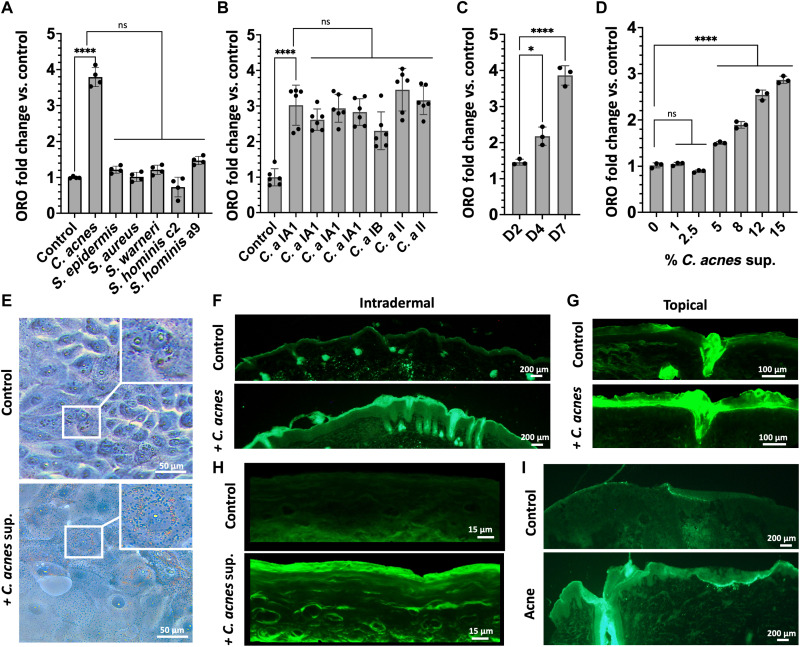
Fig. 1. C. acnes induces increased lipid staining in mouse and human skin.
(A) Oil Red O staining (ORO) of total lipids in NHEKs after treatment with sterile supernatants from media conditioned by the growth of different species of bacteria commonly found on human skin or (B) different C. acnes strains (C. a). (C) Oil Red O quantification of total lipids in NHEKs at days 2 (D2), 4 (D4), and 7 (D7) after exposure to 15% of sterile supernatant from C. acnes CM. (D) Dose-response at day 4 Oil Red O staining of total lipids in NHEK after treatment with different concentrations of sterile supernatant from C. acnes conditioned culture media. (E) Oil Red O lipid staining of NHEKs with and without sterile supernatant from C. acnes conditioned culture media. (F) Bodipy lipid staining of mouse skin after intradermal injection of 107 CFU/ml of C. acnes or (G) topical application of 107 CFU/cm2 of C. acnes on mice. (H) Bodipy lipid staining of reconstructed human epidermis treated with or without sterile supernatant from C. acnes CM. (I) Bodipy lipid staining of an acne lesion and nonlesional human skin. Experiments conducted were performed at least in triplicate. Not significant (ns) = P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.