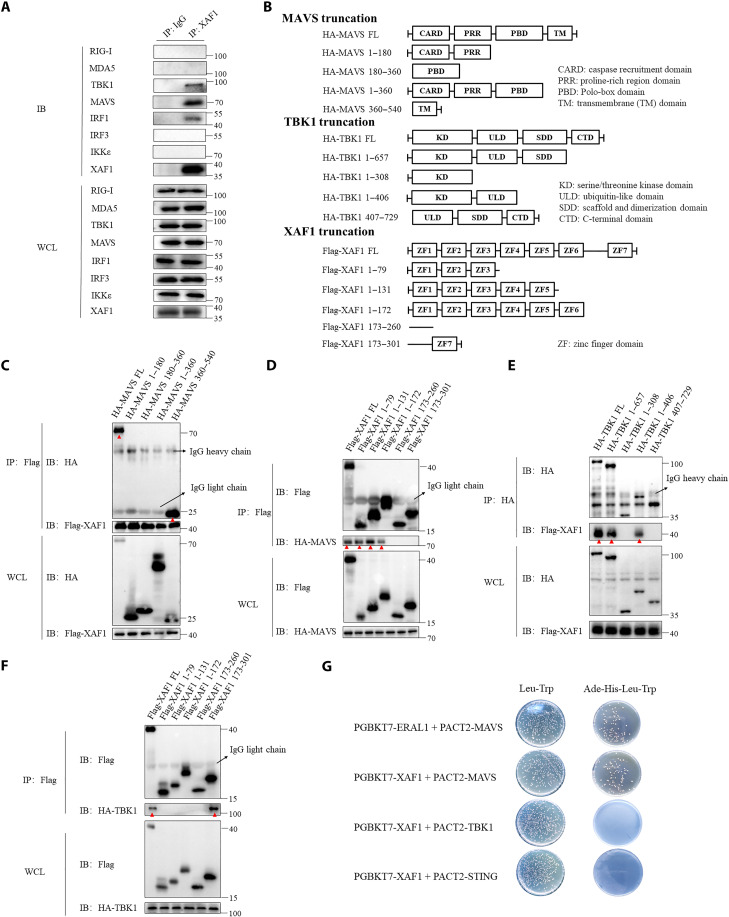
Fig. 3. XAF1 interacts with MAVS and TBK1.
(A) coIP assay analysis of the interaction between endogenous XAF1 and RIG-I, MDA-5, TBK1, MAVS, IRF1, IRF3, and IKKe in HT-29 cells. (B) Diagram detailing the series of truncations of MAVS, TBK1, and XAF1. (C and D) coIP assay analysis shows which domains of MAVS and XAF1 interacted. Red arrowheads in (C) and (D) highlight the interaction bands. (E and F) coIP assay analysis shows which domains of TBK1 and XAF1 interacted. Red arrowheads in (E) and (F) highlight the interaction bands. (G) Direct interaction of XAF1 with MAVS, STING, and TBK1 was detected by a yeast two-hybrid assay. Yeast strain AH109 was transfected with PGBKT7-XAF1, PACT2-MAVS, or PACT2-STING and inoculated on the indicated media for 3 days. ERAL1 and MAVS were introduced as positive controls. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. WCL, whole-cell lysate; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.