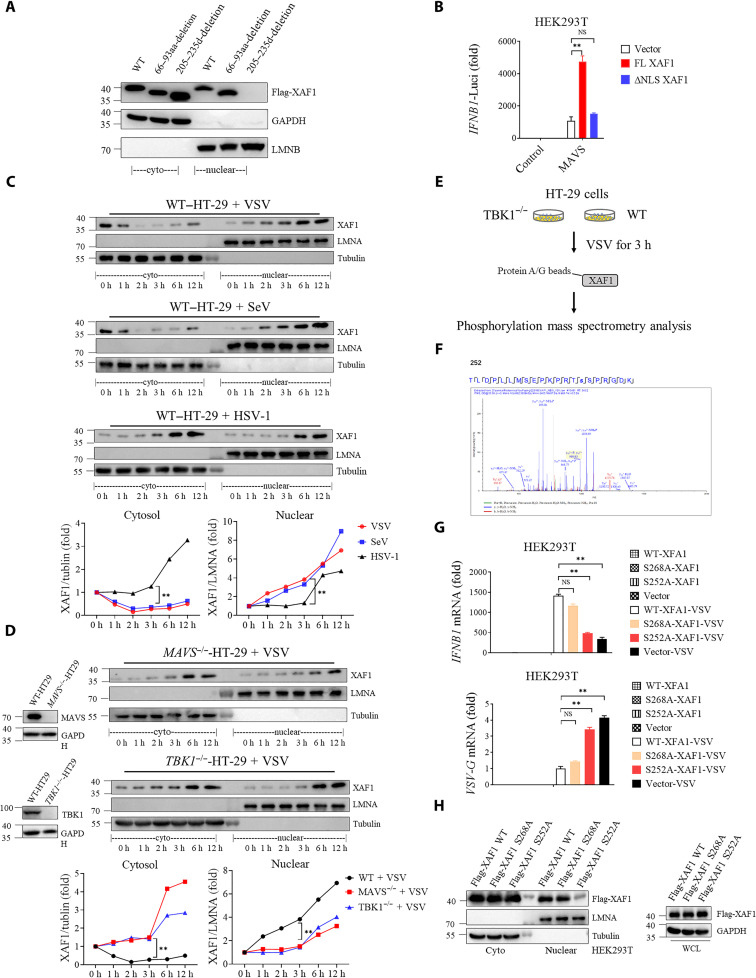
Fig. 4. TBK1 phosphorylates XAF1 at S252 and promotes early nuclear translocation of XAF1.
(A) Putative NLS sequences of XAF1 were screened. Western blotting was used to analyze the protein distribution in cytoplasm and nucleus. (B) Luciferase activity in HEK293T cells transfected with 50 ng of pRL-TK reporter and 50 ng of luciferase reporter driven by promoters of genes encoding IFN-β, expression plasmids MAVS together with Vector, full length (FL), or NLS-deletion XAF1 plasmids for 24 hours. (C and D) Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were isolated, and the time course of changes in (C) XAF1 levels in each fraction after VSV, SeV, and HSV-1 infection in HT-29 cells and (D) XAF1 levels in each fraction after VSV infection in MAVS−/− (top) or TBK1−/− (bottom) HT-29 cells was tracked by Western blotting. The relative expression of XAF1 [relative to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) or LMNA (Lamin A/C)] curve shows its dynamic changes in cytoplasm and nucleus. (E) A flow chart depicting the process of coIP experiments to detect the phosphorylation site of XAF1 by TBK1 in TBK1−/− and WT HT-29 cells. (F) Phosphorylation site of XAF1 by TBK1 was identified via mass spectrometry. (G and H) HEK293T cells were transfected with indicated Vector, FL-XAF1, S252A-XAF1, and S268A-XAF1 for 24 hours. After 12 hours of VSV infection, qRT-PCR analyses of IFNB1 mRNA (top) and VSVG mRNA (bottom) were performed. Western blotting was used to analyze the protein distribution in cytoplasm and nucleus. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3) from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 [Student’s t test (B) to (D) and (G)]. Data are representative of two [(E) and (F)] or three [(A) to (D) and (G) and (H)] independent experiments with similar results. aa, amino acid.