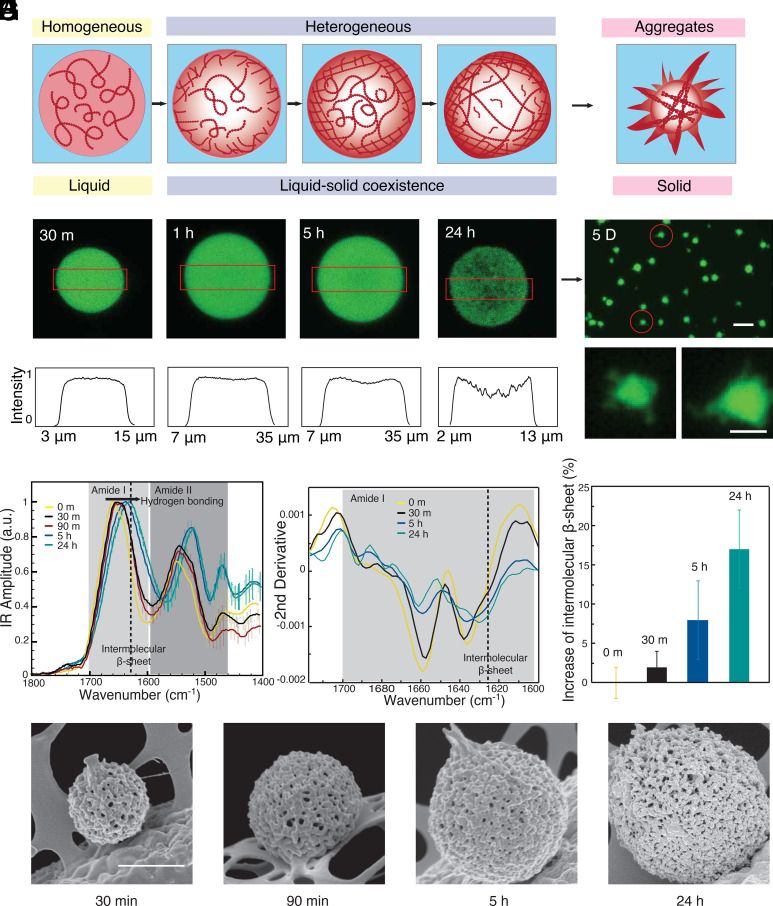
Fig. 1.
Spatially inhomogeneities during the aging of FUS condensates. (A) The FUS protein undergoes liquid–liquid phase separation in response to changes in ionic strength. During subsequent maturation, the density within the condensates changes from homogenous to locally heterogeneous (B) Confocal images of the density distribution within a condensate during maturation at 30 min, 1 h, 5 h, and 24 h. (C) The fluorescence intensity profile from confocal microscopy at the center plane of the condensates (red boxes indicate the evaluated area in B). (D) Fluorescence images of fibrillar aggregates formed at the final stages of the liquid-to-solid transition after maturation for 5 d. (Scale bars are 20 and 5 μm in Top and Bottom.) (E) Bulk IR absorption spectra and (F) their second derivatives of condensates with different aging times. (G) Relative increase in intermolecular β-sheet with aging time, error bar: CI deriving from the integration algorithm of the second derivative. (H) SEM images of condensate with different maturation times. (Scale bar, 1 μm.)