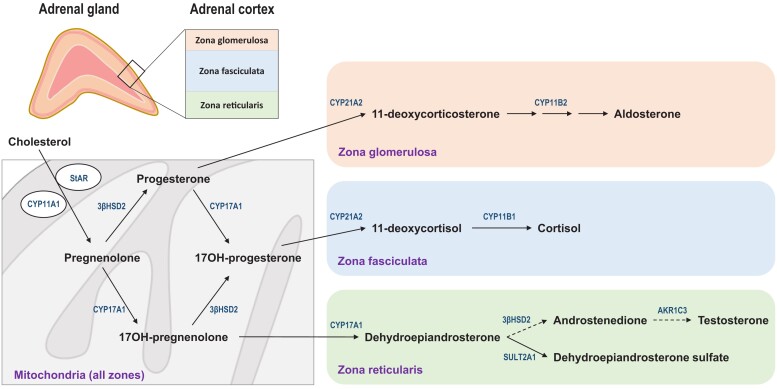
Figure 3.
Initiation of steroidogenesis and downstream metabolism in the 3 zones of the adrenal cortex. Cholesterol in the outer mitochondrial membrane is converted to pregnenolone via the side-chain cleavage enzyme CYP11A1 on the inner mitochondrial membrane in a process that requires the StAR for maximal efficiency. Nascent pregnenolone is either converted to progesterone via the 3βHSD2 or 17-hydroxylated via CYP17A1. In the zona glomerulosa, absence of CYP17A1 and presence of 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2) and aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) limits metabolism to the mineralocorticoids DOC and aldosterone. In the zona fasciculata, 17OHP is sequentially 21- and 11β-hydroxylated to cortisol, reactions that CYP21A2 and CYP11B1 catalyze, respectively. In the zona reticularis, pregnenolone metabolism is limited to CYP17A1, first to 17-hydroxypregneneolone and then to DHEA, the latter via the 17,20-lyase activity. Most DHEA is sulfonylated to DHEAS via the sulfotransferase SULT2A1, but lesser amounts of DHEA are converted to A4 and then via AKR1C3 to testosterone. Note that the pathways to cortisol and aldosterone—but not the pathway to A4—require CYP21A2. Abbreviations: 3βHSD2, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/isomerase type 2 enzyme; A4, androstenedione; AKR1C3, aldo-keto reductase type 1C3; DHEA, dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEAS, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate; DOC, 11-deoxycorticosterone; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein.