Fig. 3.
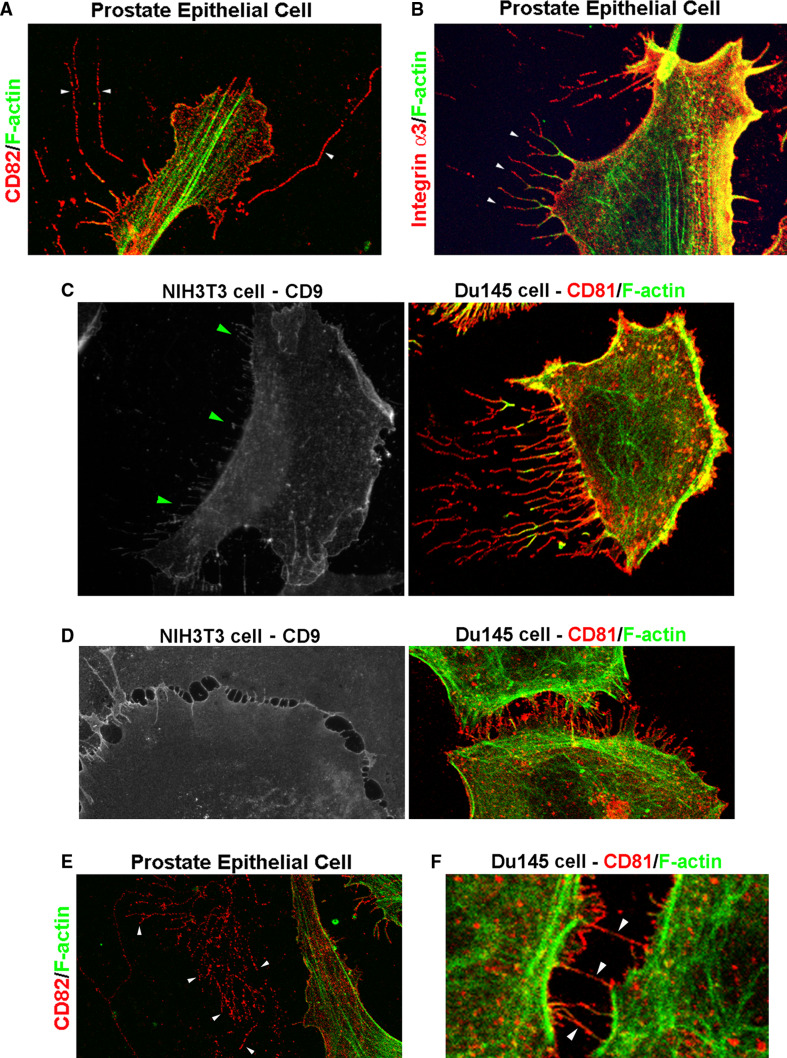
Tetraspanin-containing membrane tubular structures (memtubs) in various cellular behaviors. a Tetraspanin CD82 was detected in thin and long micro-memtubs of human prostate epithelial cells. b Tetraspanin-associated proteins such as integrin α3 are found in the micro-memtubs, as indicated by the arrowheads, of human prostate epithelial cells. Although actin fibers were detectable in these micro-memtubs, F-actin was present in the cell-proximal portion of these structures. Notably, the integrin α3-positive micro-memtubs are branched. c Tetraspanins are found in the micro-memtubs associated with cell retraction during cell movement or cell front-rear polarization. For example, CD9-positive micro-memtubs are present at the trailing edge of migrating NIH3T3 murine fibroblast cells, as indicated by the arrowheads; while CD81-positive micro-memtubs are present at the trailing edge of migrating Du145 human prostate cancer cells. The memtubs formed at the leading edges are typically filopodia. d Tetraspanins CD9 and CD81 are found in the micro-memtubs during the formation of the cell-cell adhesion zipper in NIH3T3 and Du145 cells, respectively. e The micro-memtubs can be remained on extracellular matrices after cells have either moved away or become detached. The image shows the wreckage of CD82-positive micro-memtubs, as indicated by the arrowheads. Note that F-actin is deprived of these wreckages. f Tetraspanin CD81-positive micro-memtubs form nanotubules between Du145 cells