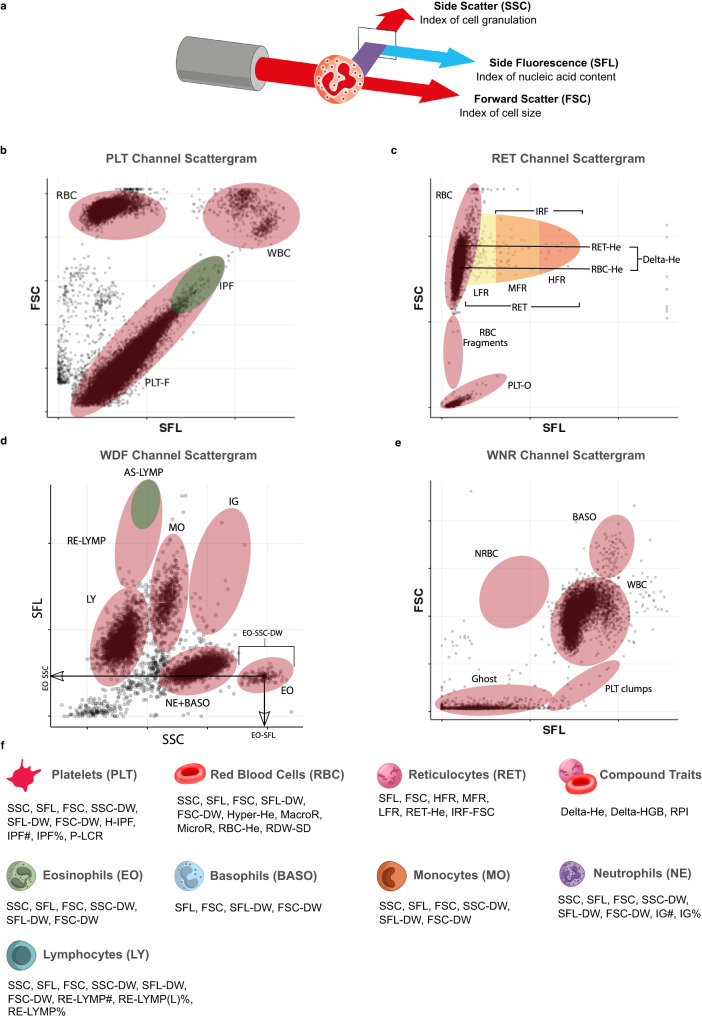
Fig. 1. Flow-cytometry traits measured by the Sysmex XN-1000 haematology analyser (adapted from Sysmex XN-1000 Manual104).
a Schematic of a granulocyte cell passing through the laser of the internal flow-cytometer of the analyser. The instrument measures the intensities of incident light scattered sidewise (SSC, cell complexity/granularity) by the cell and forward (FSC, cell volume) by the cell and the intensity of the light which is absorbed by the cell and fluoresced at a new wavelength (SFL, cell nucleic acid content). b–e Cytometry scattergrams from an arbitrary participant in the INTERVAL study: 2-dimensional projections of the cell level intensity data (SSC, SFL, FSC) measured in each of the four XN-1000 flow-cytometry channels active for the INTERVAL study: PLT-F (platelet flow) channel (b), RET (reticulocyte) channel (c), WDF (white cell differential) channel (d), WNR (white cell and nucleated red cell) channel (e). Many of the traits correspond to averages or distribution widths (DWs) of cell level measurements in scattergram regions (indicated approximately by ellipses) occupied by cells of particular types. This is illustrated for three eosinophil traits (in panel d). Supplementary Data 2 contains a full description of the measurement procedure for each trait. f The 63 cytometry traits classified by the type of cells which they measure: platelets (PLT), mature red blood cells (RBC), reticulocytes (RET), neutrophils (NE), eosinophils (EO), basophils (BASO), monocytes (MO) and lymphocytes (LY). The three compound traits (Delta-HE, Delta-HGB, and RPI) depend on measurements of both mature red cells and reticulocytes. We thank Joanna Westmoreland for the artwork in (a) and (f).