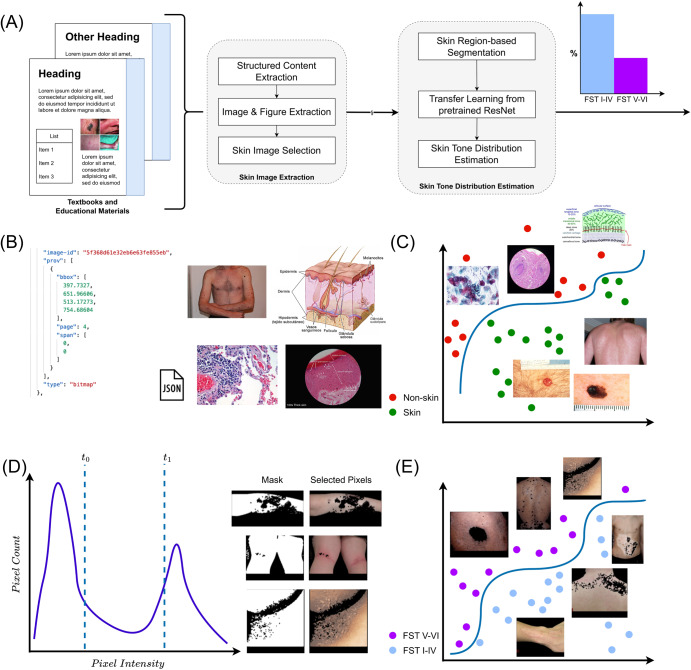
Fig. 1. STAR-ED framework overview.
A STAR-ED framework takes academic materials (e.g., in .pdf format) as input followed by extraction of skin images in the given academic material. Specifically, image pixels that are identified as skin are then utilized to estimate the skin tone category. B Corpus Conversion Service (CCS) (7) is an existing document ingestion tool employed to parse different document entities, such as all images and tables in the data. We extracted all images using the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) (8); output from the ingestion step contains the coordinates and page number of identified images. C Since our focus is on images related to skin diseases, non-skin images (e.g., graphical illustrations and pathology images) are discarded using an XGBoost (9) classifier. D For each image depicting skin, we masked out non-skin related pixel regions in the foreground and background (e.g., pixels of clothes, laboratory equipment). We employ color-based skin pixel segmentation that extracts pixels that meet a predefined threshold. E Finally, the segmented skin regions are fed into a pre-trained deep learning framework, i.e., ResNet17 fine-tuned as described in Materials and Methods, to estimate the skin tone category as either light (FST I–IV) or dark (FST V–VI). Images adapted from Wikimedia commons.